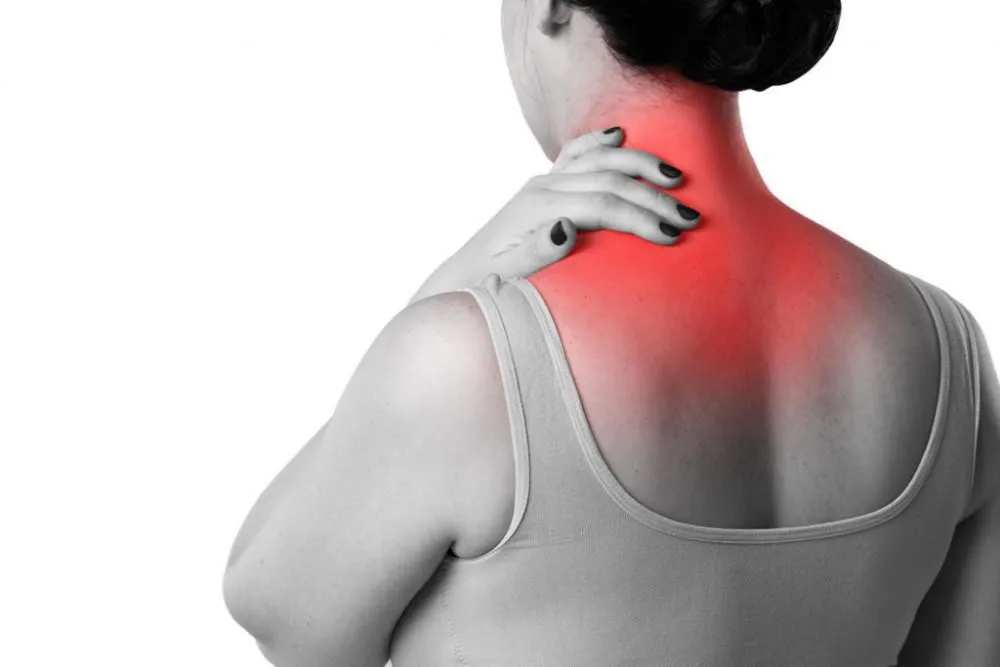
Achilles Tendinitis: Symptoms, Causes, Prevention
Achilles tendinitis is a prevalent overuse injury that impacts the Achilles tendon—a critical band of tissue that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone.
Sept. 21, 2023, 3 min read, Articles
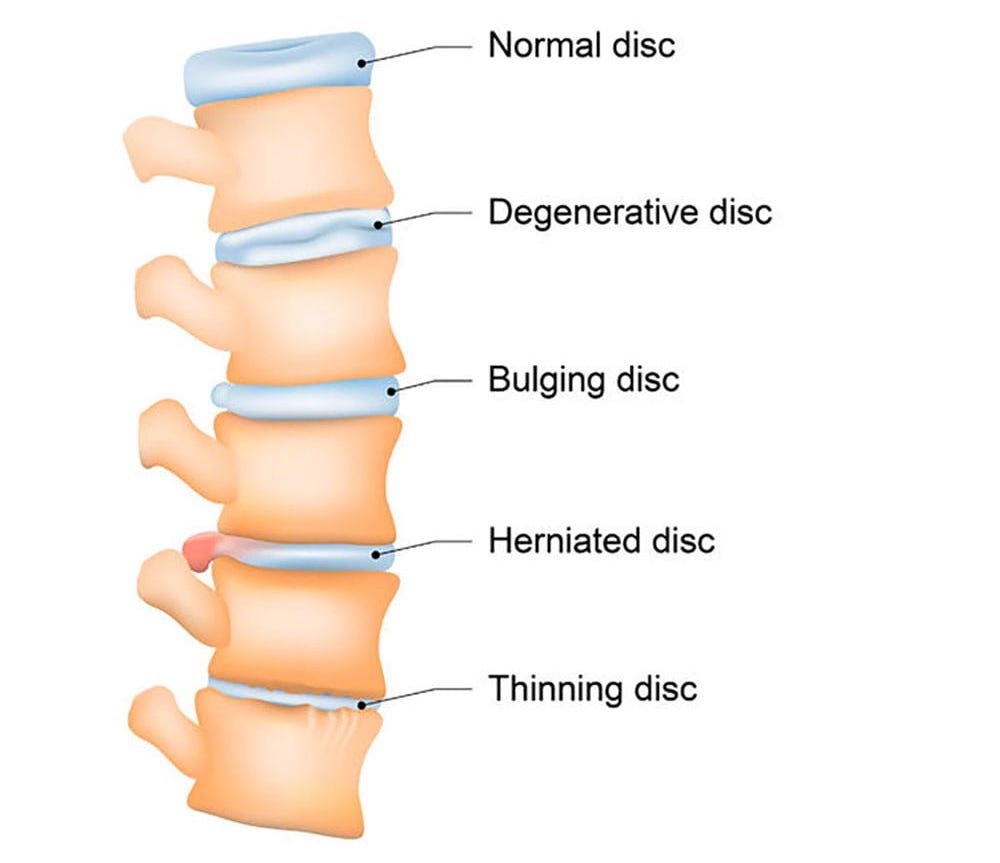
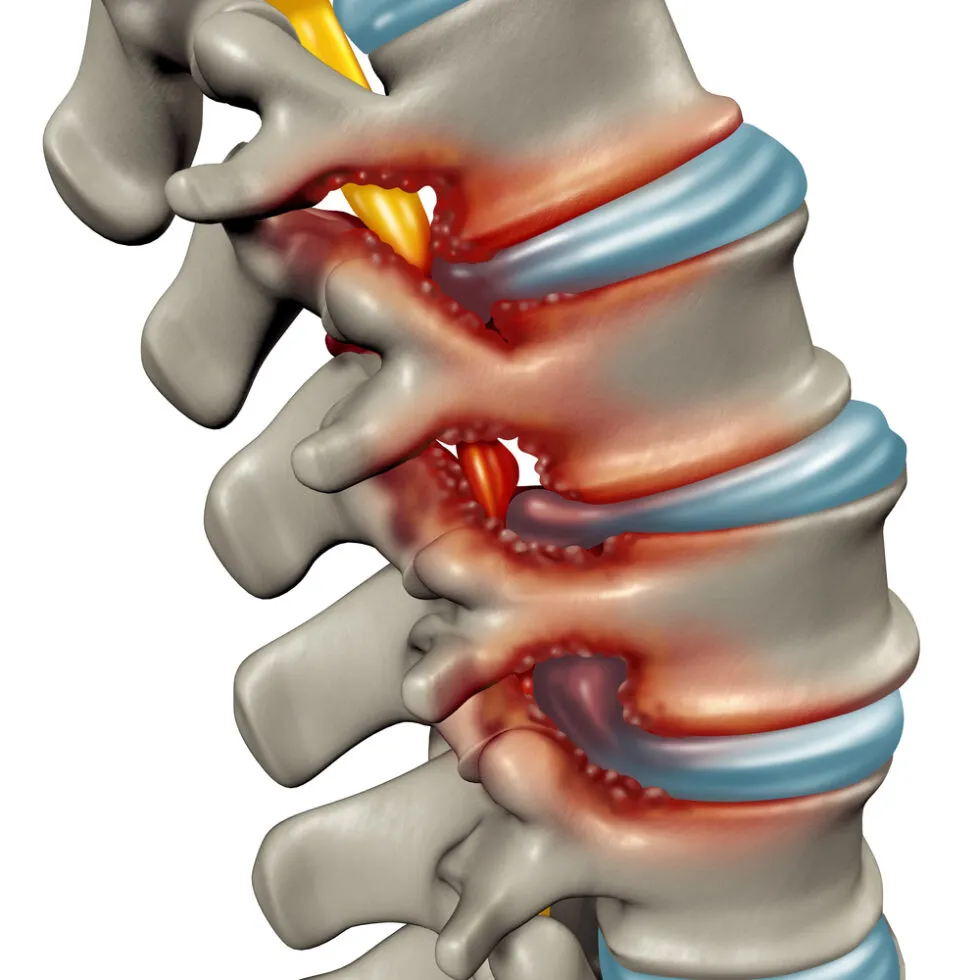
Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD) is a common condition that affects the intervertebral discs in the spine. In this comprehensive article, we will explore Degenerative Disc Disease, examining its causes, symptoms, and the effective treatment options, with a special focus on the therapeutic techniques provided by physiotherapy and osteopathy.
Degenerative Disc Disease is not truly a disease but rather a natural part of the aging process. It occurs when the discs between the vertebrae in the spine begin to deteriorate, leading to various spinal issues.
Aging: As we age, the discs lose water content and become less flexible, leading to degeneration.
Genetics: A family history of DDD can increase the risk.
Injury: Trauma to the spine can accelerate disc degeneration.
Smoking: Smoking is associated with faster disc degeneration.
Obesity: Excess body weight places additional stress on the spine, contributing to DDD.
Symptoms of DDD can vary but often include:
Pain: Chronic low back pain or neck pain that worsens with movement.
Radiating Pain: Pain that may radiate into the arms or legs if nerve compression occurs.
Numbness and Tingling: Sensations of numbness, tingling, or weakness in affected areas.
Reduced Mobility: Limited range of motion due to pain and stiffness.
The treatment of DDD involves a holistic approach, with physiotherapy and osteopathy offering valuable therapeutic techniques:
Exercise Programs: Physiotherapists design tailored exercise regimens to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine and improve flexibility.
Pain Management: Techniques like hot/cold therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation to alleviate pain and inflammation.
Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques to improve spinal alignment and mobility.
Posture and Ergonomics: Guidance on maintaining proper posture and ergonomics to reduce strain on the spine.
Manual Techniques: Osteopathic practitioners use manual manipulation to enhance spinal alignment and circulation, potentially reducing pain.
Whole-Body Assessment: Osteopathy considers the interconnectedness of the body, addressing any structural issues contributing to DDD.
Medications: Pain relievers, muscle relaxants, or anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed.
Injections: Epidural steroid injections may provide temporary relief from pain.
Surgery: In severe cases, surgical interventions like spinal fusion or artificial disc replacement may be considered.
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking can promote spine health.
Proper Lifting Techniques: Use correct lifting techniques to reduce the risk of spinal injuries.
Ergonomic Workspaces: Ensure workspaces are ergonomically designed to reduce strain on the spine.
Degenerative Disc Disease is a common issue associated with aging, but with the right treatment approach, including physiotherapy and osteopathy, individuals can find relief from their symptoms and improve their spinal health. If you suspect you have DDD, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan.
Achilles tendinitis is a prevalent overuse injury that impacts the Achilles tendon—a critical band of tissue that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone.
Back pain is a prevalent and often debilitating condition that can affect individuals of all ages and walks of life.
Arthritis is a common and often painful condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It's not a single disease but rather a group of more than 100 different types of joint-related conditions.
Ankle injuries are prevalent in the world of sports and can be a significant setback for athletes.
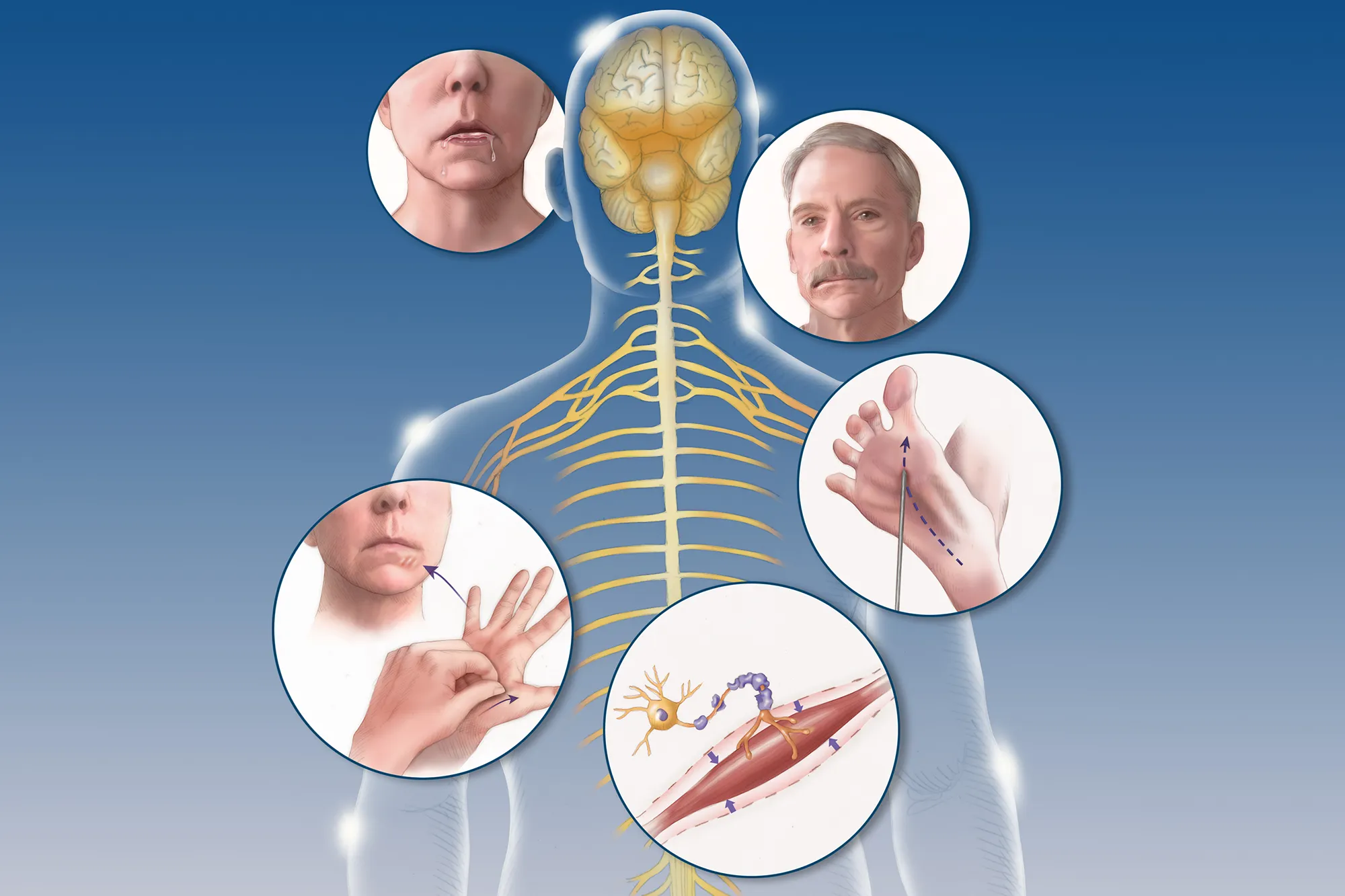
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), often referred to as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord.
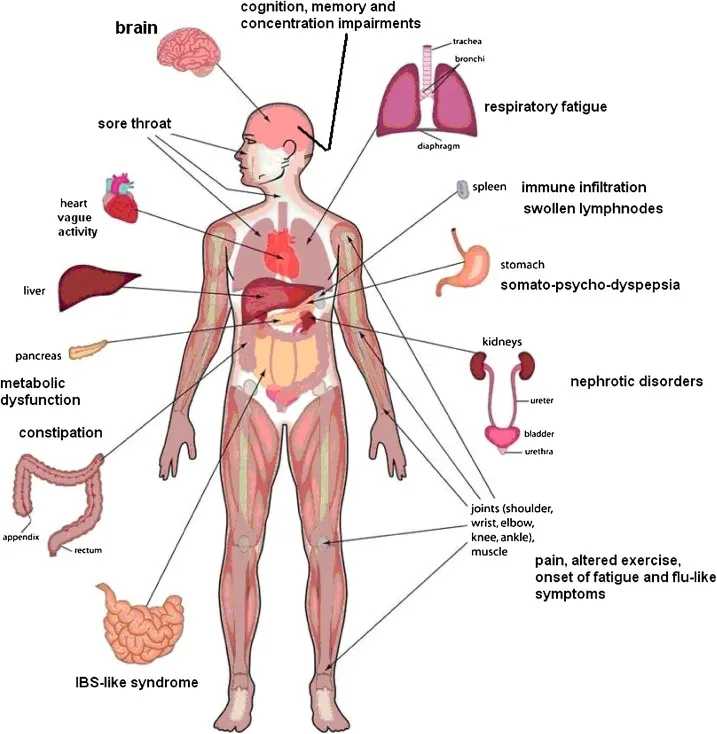
Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) is a perplexing and debilitating condition that impacts individuals, often altering their daily lives and challenging conventional understanding.
Muscular dystrophy encompasses a group of diseases leading to progressive muscle weakness and loss of muscle mass. The development of abnormal genes disrupts the production of necessary proteins crucial for healthy muscle function.
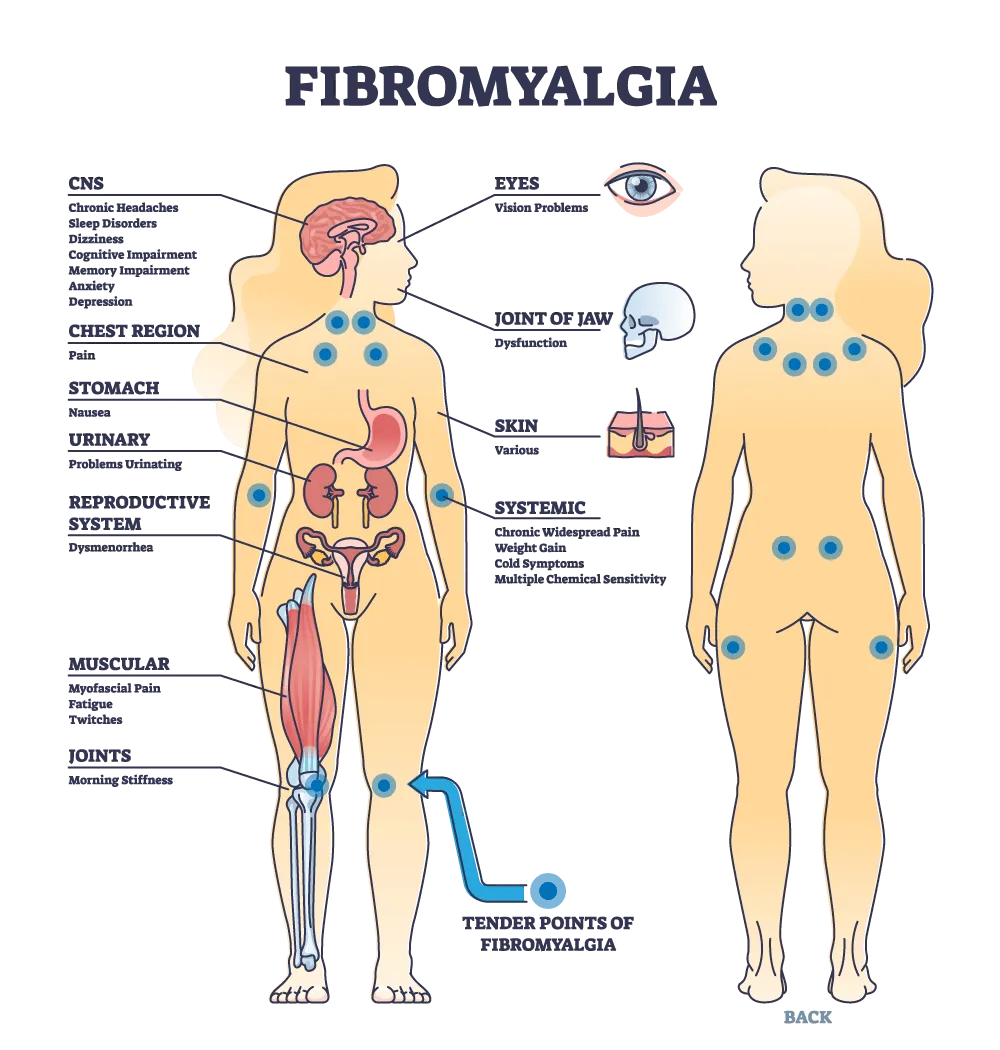
Fibromyalgia stands as a complex and often misunderstood condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbances
Bunions, medically referred to as "hallux valgus," are a common and often painful foot deformity that affects the joint at the base of the big toe.
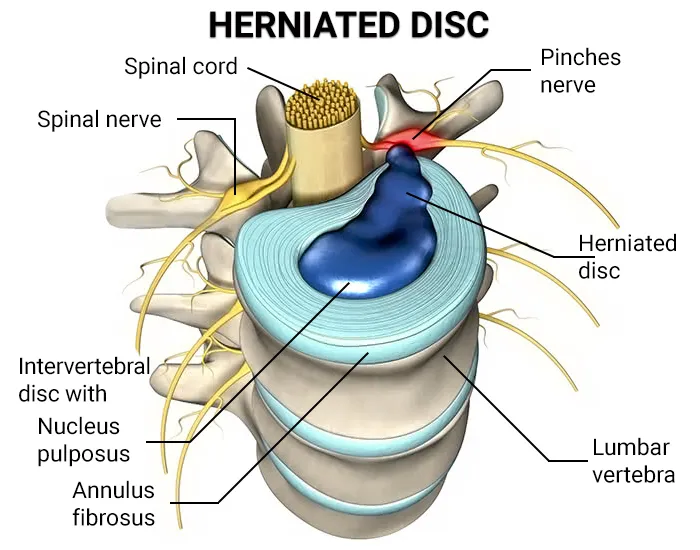
Herniated disc symptoms can be debilitating, causing pain, numbness, and mobility limitations.
A heel spur is a bony growth that pokes out below your back heel bone inside of your foot. Heel spurs happen when stress and strain damages your foot ligaments.
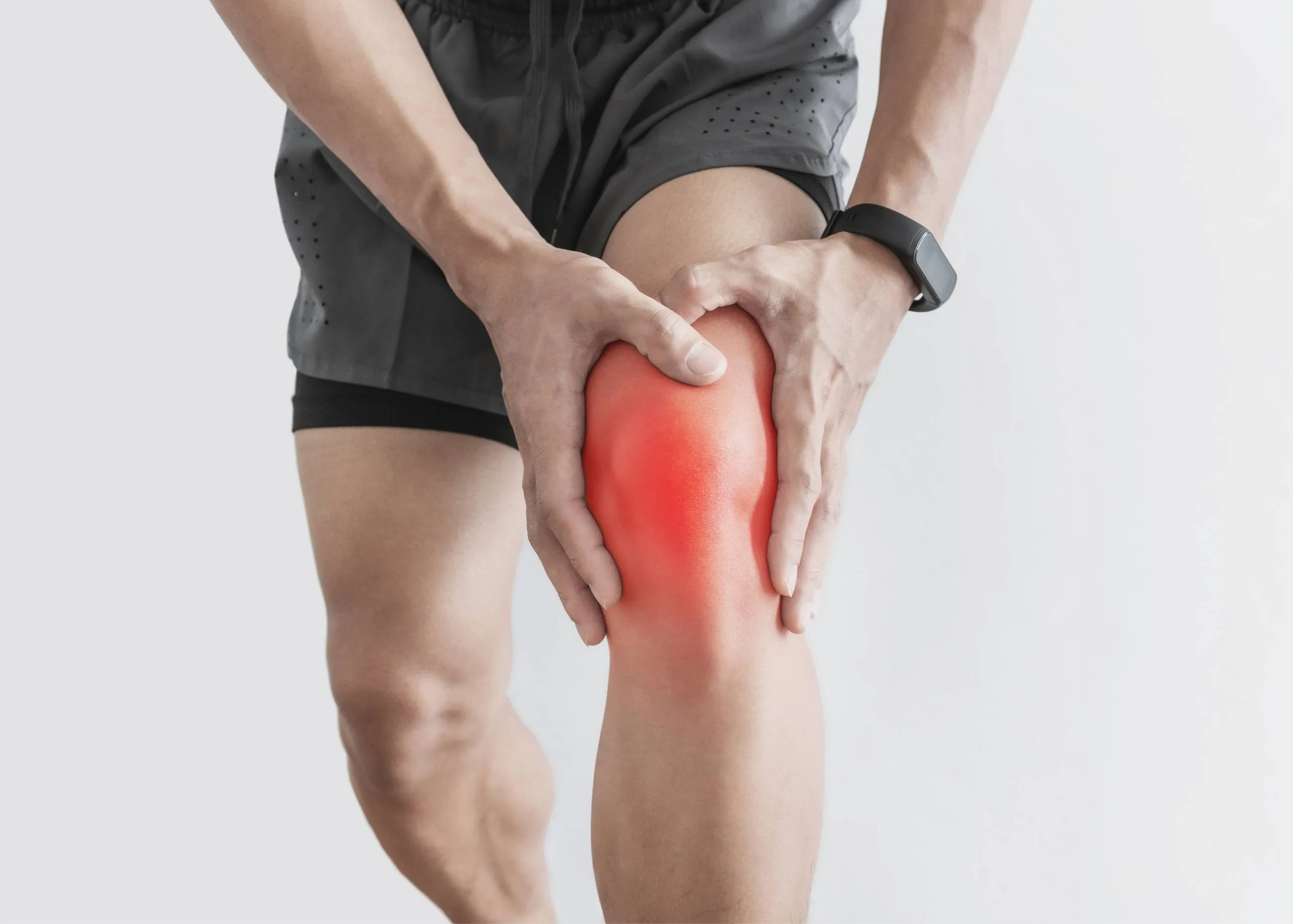
Knee pain is a widespread issue that can significantly impact a person's mobility and quality of life.Knee pain is a widespread issue that can significantly impact a person's mobility and quality of life.
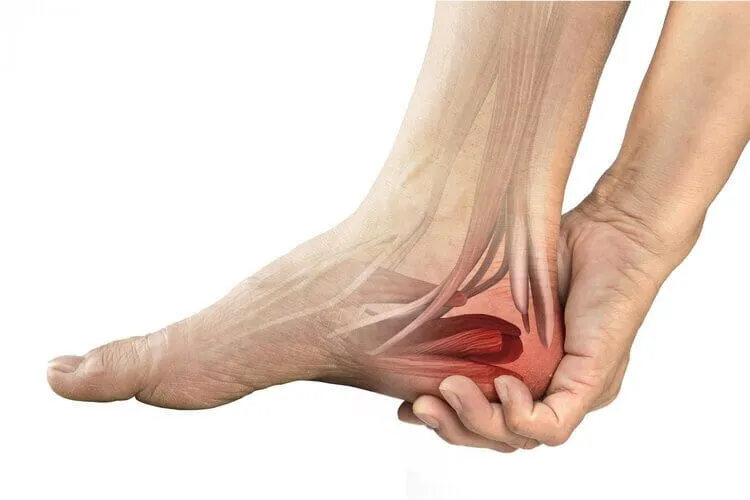
Heel pain can be a nagging and uncomfortable issue that affects many people. In this article, we will explore the various causes of heel pain, common symptoms associated with it, and the available treatments that can help you find relief and get back to your active lifestyle.
Military Neck, also referred to as Cervical Kyphosis, is a condition that affects the natural curvature of the cervical spine, resulting in the loss of its typical curve.
Migraines and headaches are prevalent neurological disorders that affect a significant portion of the population.

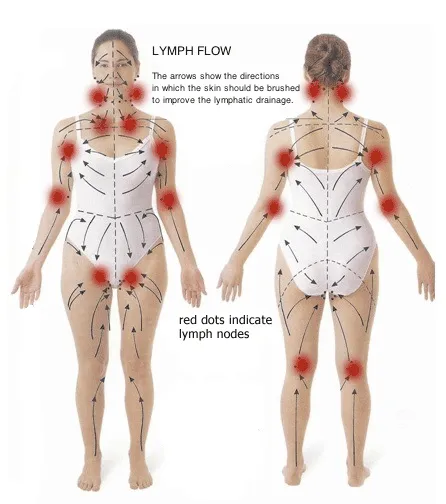
Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid, leading to persistent swelling, typically in the arms or legs.
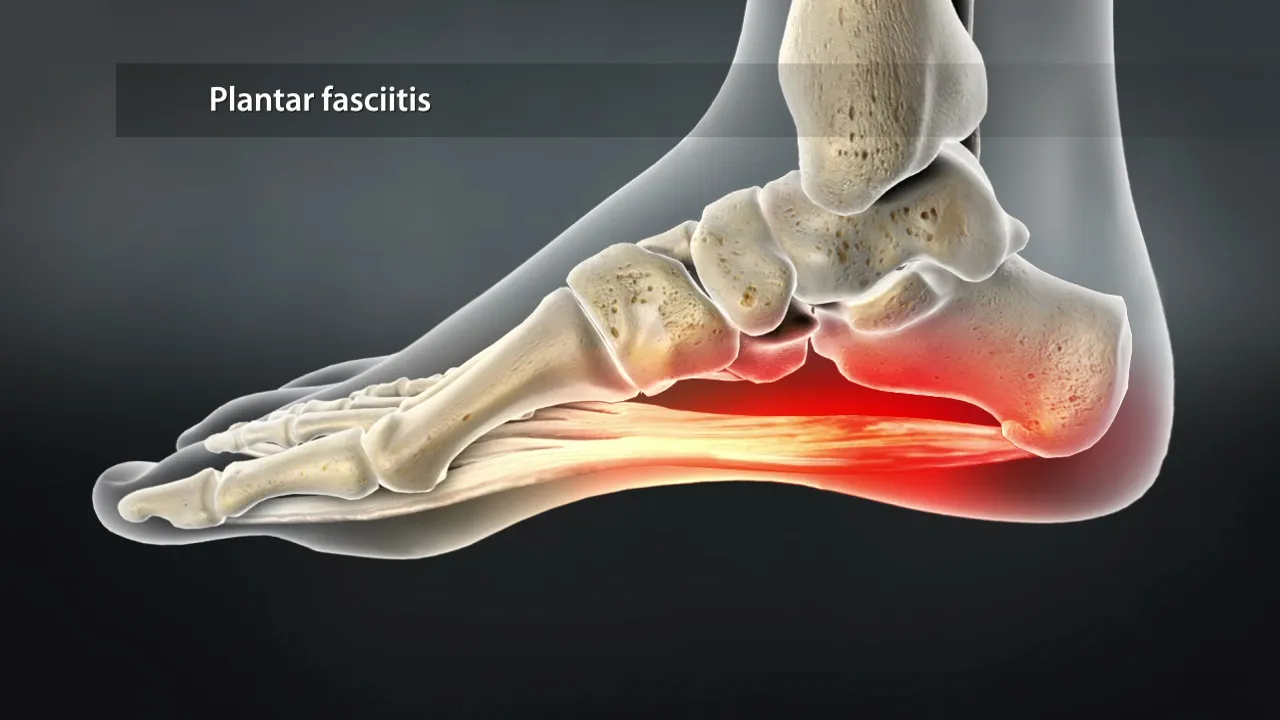
Plantar fasciitis is a common and often painful foot condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
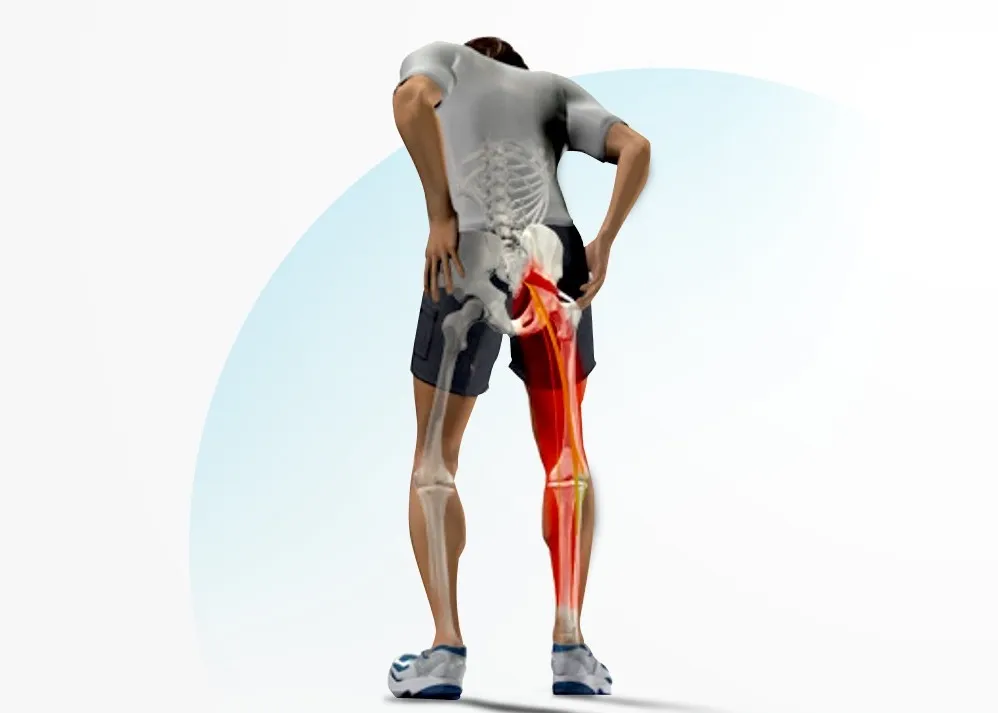
Piriformis syndrome is a perplexing condition, often overshadowed by more common sources of hip and lower back pain.
motor vehicle accidents (MVA) can result in a wide range of injuries, from minor bruises to severe trauma. in the aftermath of such incidents, seeking prompt medical attention is crucial for assessing and addressing any injuries sustained.

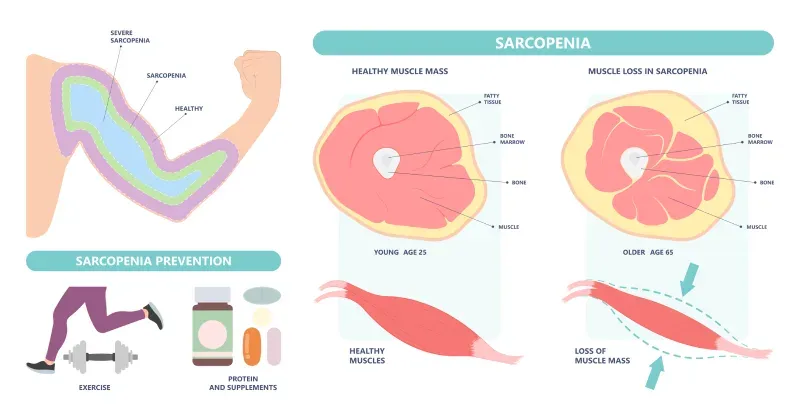
Sarcopenia is the gradual loss of muscle mass that can affect people in their 30s and beyond. WebMD explains its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatments.
Spinal stenosis, a prevalent spinal condition, is characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal, leading to discomfort and neurological symptoms.
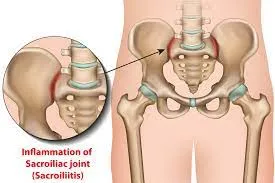
The sacroiliac joint, a crucial junction between the sacrum and the ilium bones in the pelvis, plays a pivotal role in supporting the weight of the upper body.
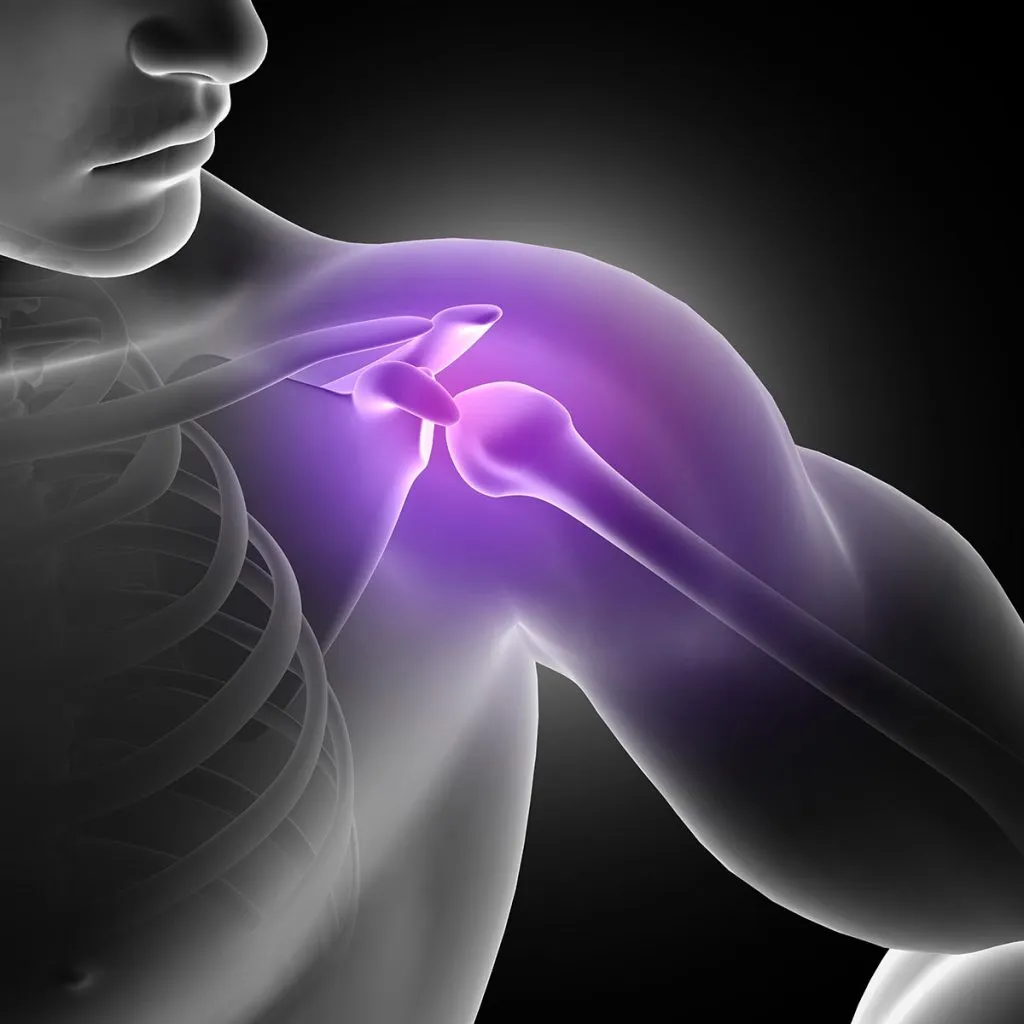
A rotator cuff injury can be a painful and limiting condition, impacting the functionality of the shoulder.
Suffering from lower back pain from sitting? It could be from poor ergonomics in your workplace. Learn more with these tips for how to alleviate pain from sitting.

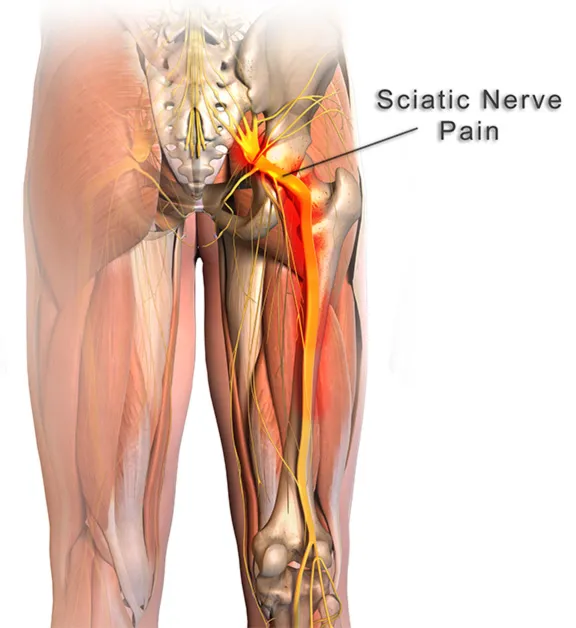
Sciatica is a painful and often debilitating condition that affects numerous individuals worldwide.
Gluteal tendinopathy is a condition that affects the tendons in the gluteal region, leading to pain and restricted mobility.
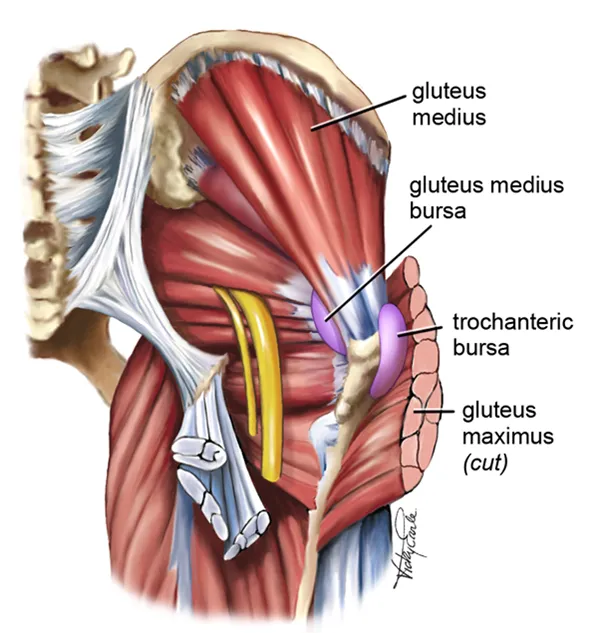
Tennis Elbow, also known as Lateral Epicondylitis, is a painful condition that affects the tendons in the forearm, causing discomfort and limited mobility in the elbow and wrist.

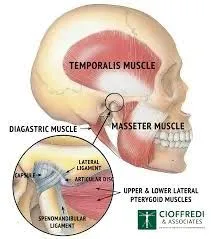
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) serves as a pivotal mechanism, allowing us to perform everyday activities such as speaking, chewing, and yawning with ease. However, when this complex joint encounters issues, it can lead to Temporomandibular Joint Syndrome (TMJ syndrome).
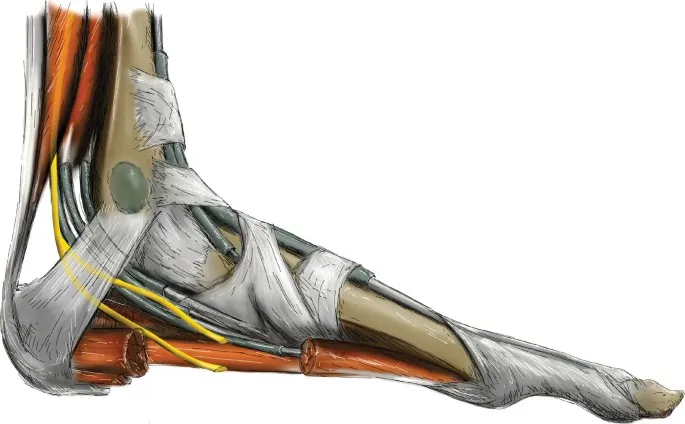
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome (TTS) is a common and often painful condition affecting the tarsal tunnel—a narrow passage in the ankle.
Explore the impact of time-restricted eating on heart health. Learn about the connection between diet and cardiovascular risk.
Most cases of foot or ankle pain are short term and are caused by soft tissue injuries, such as sprains or strains. You can usually ease the pain yourself But see York Rehab Clinic if the pain does not improve.
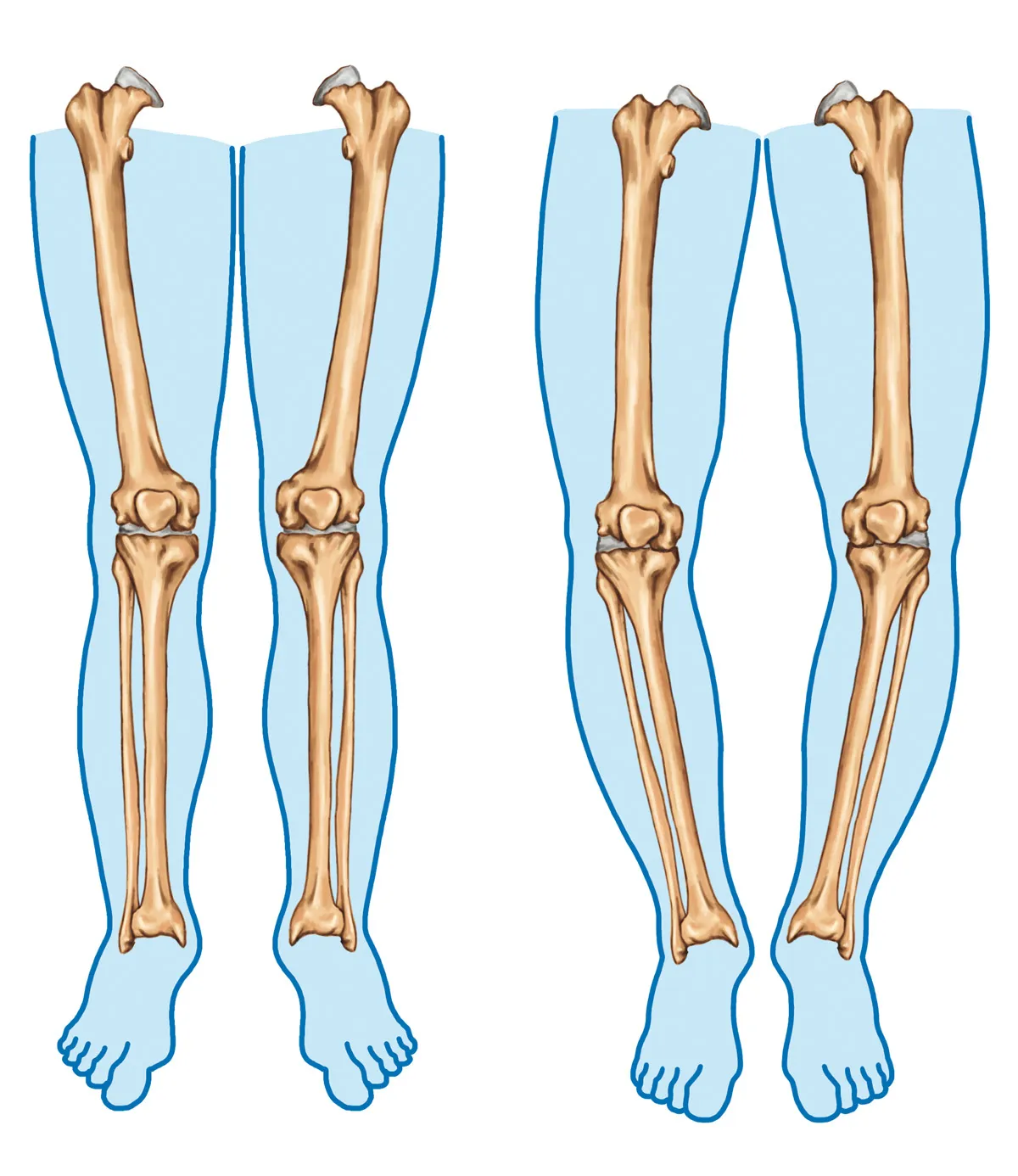
Bow legs is a genetic condition where the knees bow outward when standing. Learn its symptoms and causes at York Rehab Clinic.
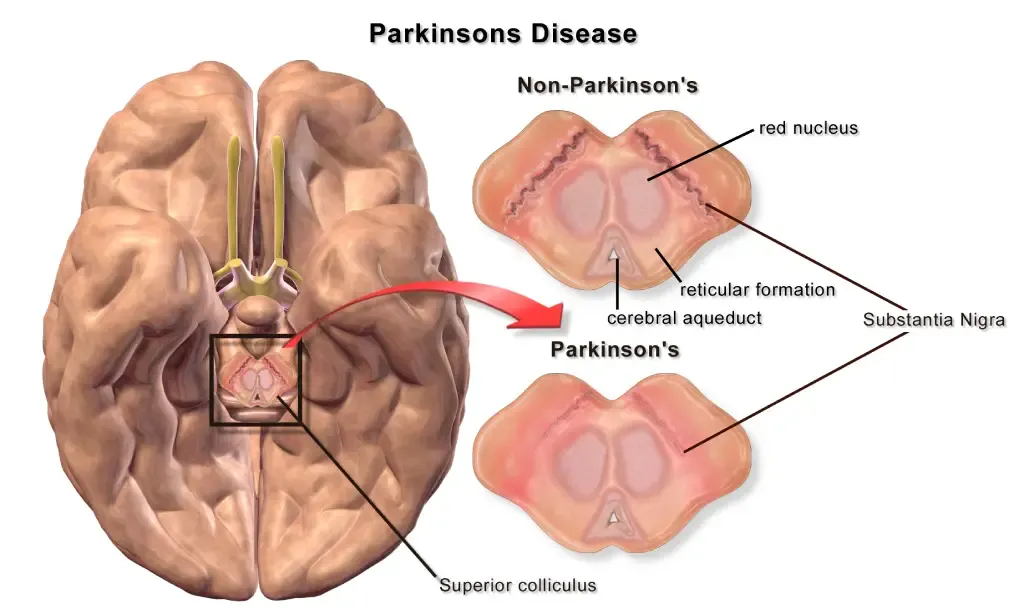
This article explores the complexities of Parkinson’s Disease and sheds light on the therapeutic benefits offered by osteopathy and physiotherapy.
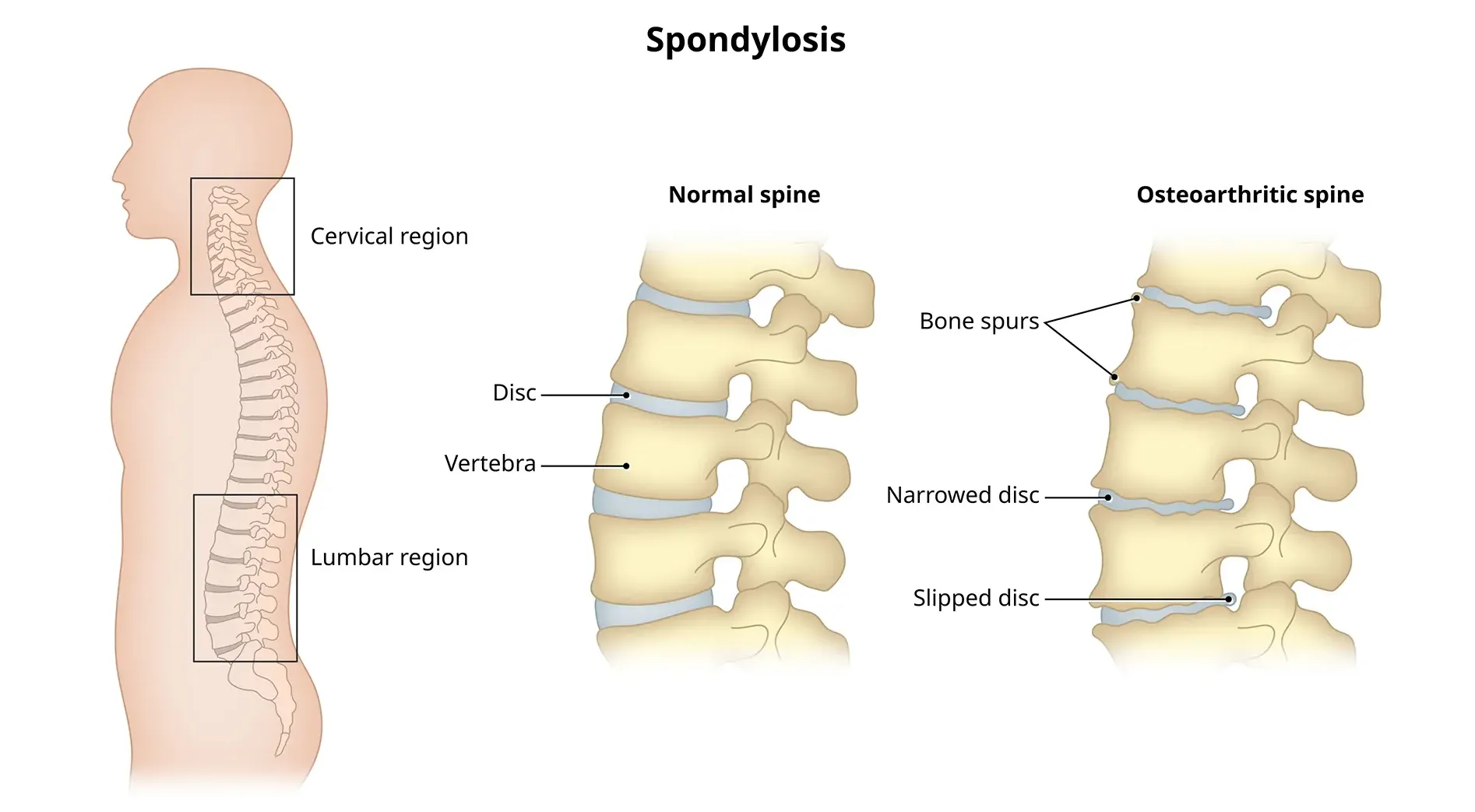
Cervical spondylosis, a prevalent condition, unfolds as a result of wear and tear on the spinal discs in the neck.
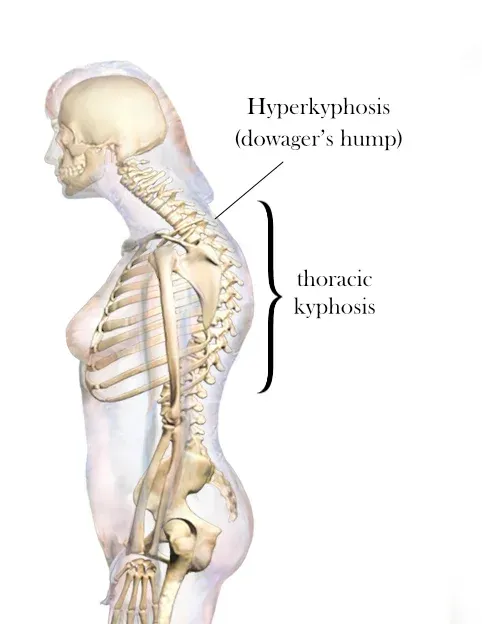
A dowager’s hump, a curve at the base of your neck, can cause extreme fatigue, back pain and headaches.
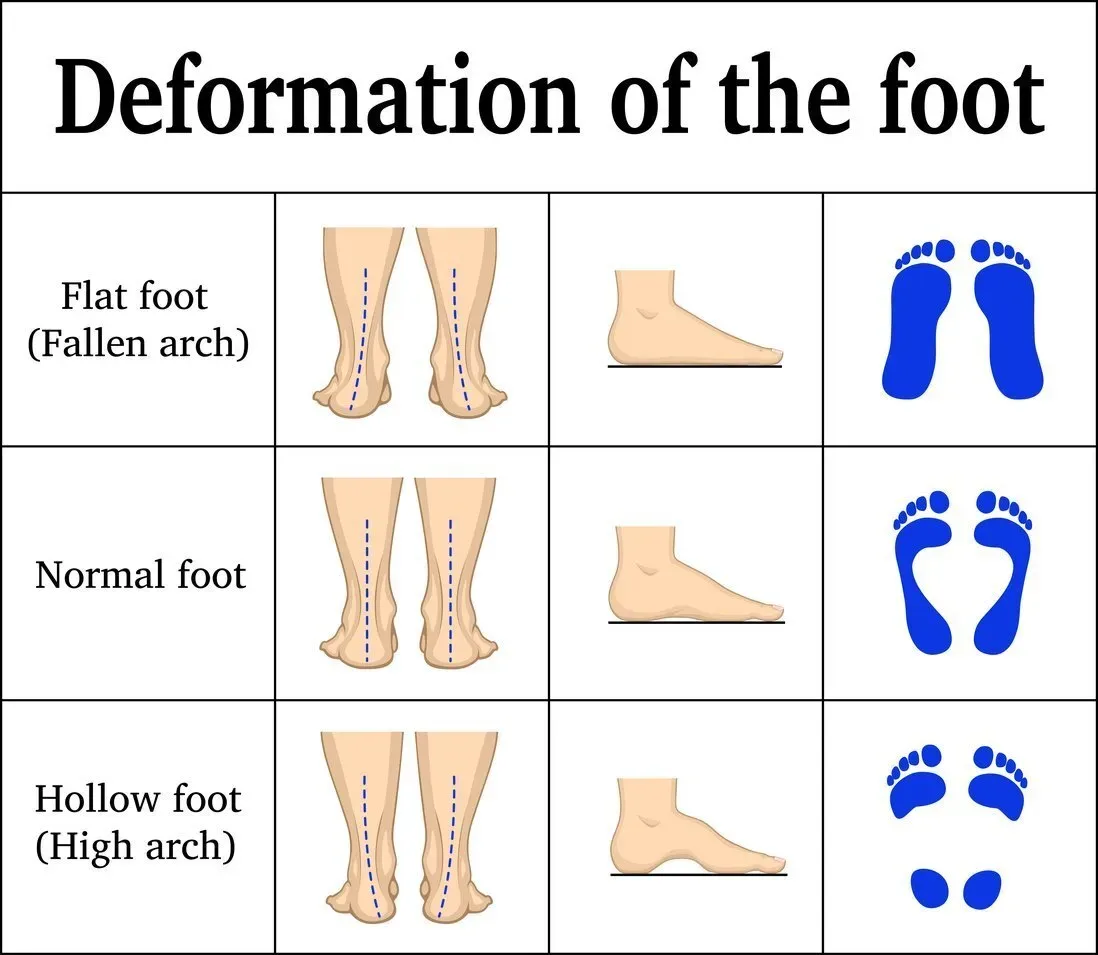
Flat feet cause pain, muscle strain, and fatigue. Treatments can ease discomfort. Symptoms include ankle pain, muscle fatigue and changes in walking.
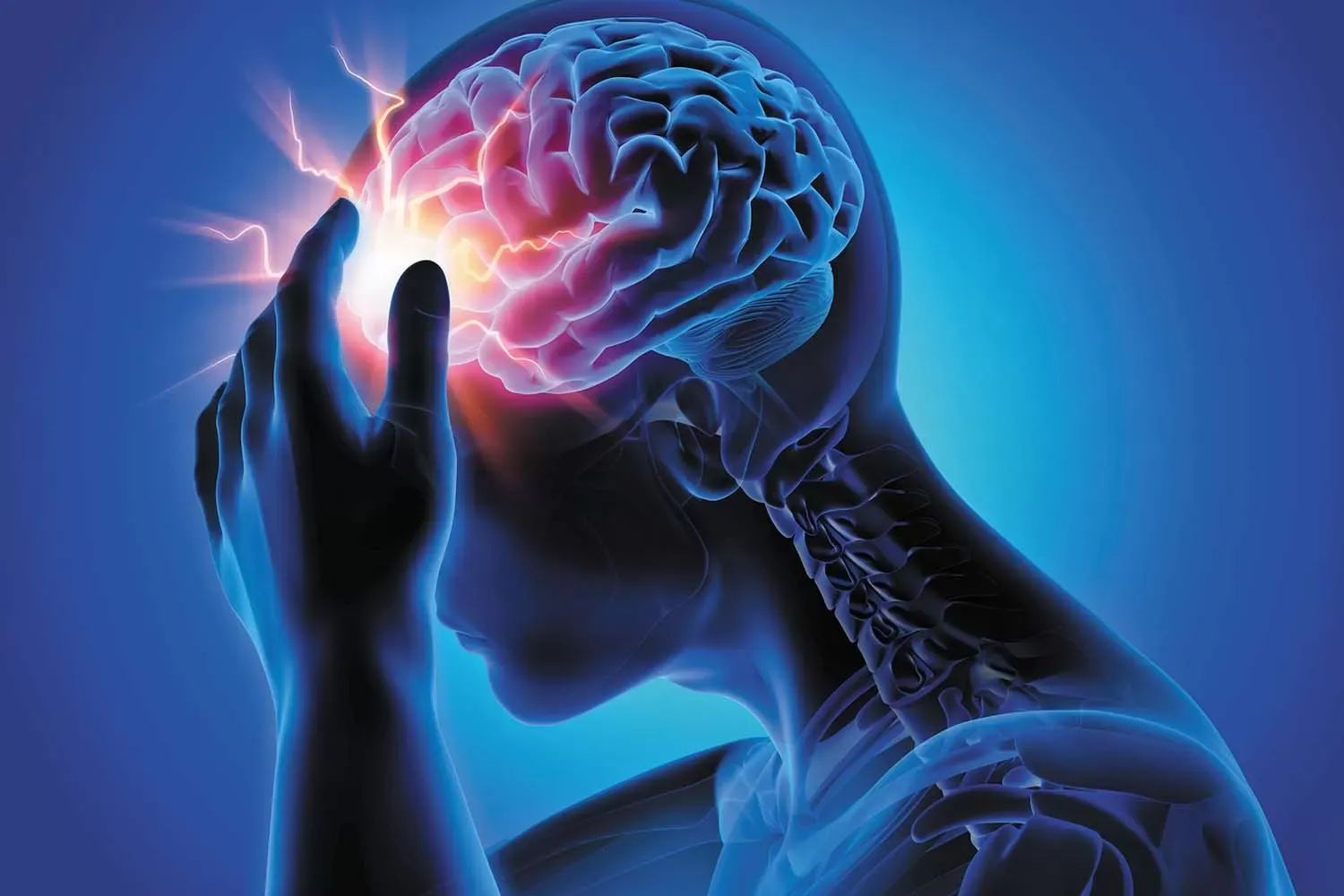
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) often results from a violent blow or jolt to the head or body, causing various physical and psychological effects.
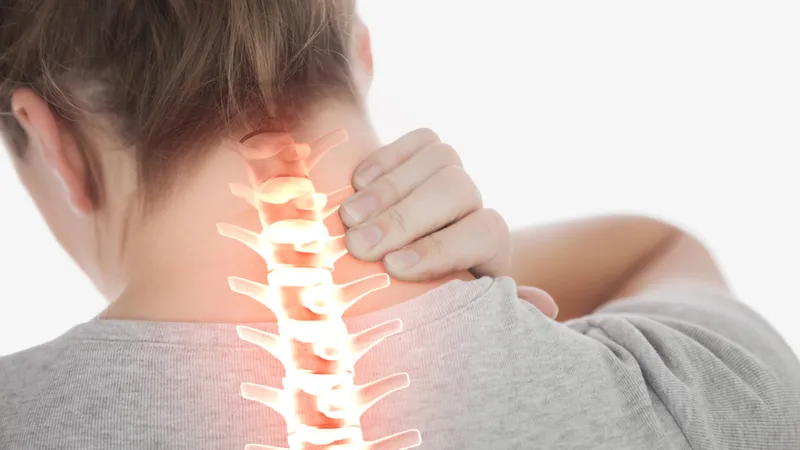
Introduction: Neck stiffness can be a discomforting and limiting condition that affects people of all ages.