Achilles Tendinitis: Symptoms, Causes, Prevention
Achilles tendinitis is a prevalent overuse injury that impacts the Achilles tendon—a critical band of tissue that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone.
Feb. 18, 2024, 7 min read, Articles
Sarcopenia, often referred to as the silent thief of muscle, is a progressive and insidious condition characterized by the gradual loss of muscle mass, strength, and functionality. Emerging predominantly in the aging population, this condition poses a substantial threat to overall health and independence. The term "sarcopenia" originates from the Greek words "sarx," meaning flesh, and "penia," denoting loss. As the aging process unfolds, the body undergoes transformative changes, ushering in a host of challenges related to muscle health. Sarcopenia affects the musculoskeletal system, becoming a major contributor to increased frailty, falls, and fractures. The consequences of this condition extend beyond the physical realm, potentially leading to hospitalizations and surgeries, thereby amplifying the risk of complications, including death. Moreover, sarcopenia's impact transcends conventional boundaries, influencing individuals with varying body compositions. In cases of high body mass index (BMI), a condition known as sarcopenic obesity may manifest. This dual challenge, combining obesity and sarcopenia, amplifies the risk of complications, surpassing those associated with each condition in isolation.
As we unravel the complexities of sarcopenia, it becomes evident that addressing this multifaceted phenomenon is crucial for preserving health, preventing adverse outcomes, and fostering a better understanding of the intricate interplay between aging, muscle health, and overall well-being.
Sarcopenia, though prevalent among diverse demographics, predominantly targets individuals aged 60 and older. This condition's prevalence increases with advancing age, underscoring its close association with the aging process. Both men and women are equally susceptible to sarcopenia, emphasizing its non-discriminatory nature across genders.The impact of sarcopenia extends beyond chronological age, as studies reveal that the rates of this condition elevate in tandem with the presence of chronic diseases. While the condition manifests across various ethnicities, research findings on affected ethnic groups may display inconsistencies.Intriguingly, sarcopenia challenges conventional expectations by extending its reach to individuals with chronic diseases. The interplay between age and health status becomes a critical factor, shaping the landscape of sarcopenia's prevalence. Therefore, understanding the nuanced dynamics of who succumbs to sarcopenia involves navigating the complex interrelationship between age, health, and demographic factors.
Understanding the prevalence of sarcopenia involves navigating a landscape marked by varying estimates and inconsistent findings. Sarcopenia's elusive nature often leads to underdiagnosis and undertreatment, contributing to the challenge of precisely determining its occurrence. Studies examining the prevalence of sarcopenia reveal a broad range, particularly among individuals aged 60 and older. The estimates fluctuate between 5% to 13% in this age group, highlighting the variability in reported figures. As we delve into the older population, aged 80 and above, the estimates broaden further, ranging from 11% to 50%. Despite these numerical variations, it is crucial to acknowledge that many individuals may not receive a formal diagnosis or appropriate treatment for sarcopenia. The underrecognition of this condition underscores the need for increased awareness, early detection, and proactive management.
Sarcopenia, the gradual loss of muscle mass, strength, and function, significantly alters the body's musculoskeletal system. This natural consequence of aging manifests as:
Understanding these aspects of sarcopenia is vital for addressing its impact on the body and adopting strategies to promote healthier aging.
Sarcopenia presents a range of symptoms that collectively contribute to a decline in overall physical well-being. Understanding these signs helps in early detection and intervention:
1. Muscle Weakness: The hallmark symptom, characterized by a noticeable reduction in muscle strength.
2. Decreased Stamina: Individuals with sarcopenia often experience a notable decline in endurance and overall stamina.
3. Slower Movement: A gradual slowing down in movement speed becomes apparent, affecting daily activities.
4. Challenges in Daily Tasks: Performing routine tasks, such as climbing stairs or rising from a chair, becomes increasingly difficult.
5. Reduced Muscle Size: Visible changes in muscle size, indicating muscle atrophy and loss of mass.
Understanding the factors contributing to sarcopenia is crucial for implementing preventive measures and targeted interventions:
1. Aging Process: The natural aging process is the primary cause, leading to a gradual loss of muscle mass.
2. Physical Inactivity: Lack of regular exercise and a sedentary lifestyle contribute significantly to the development of sarcopenia.
3. Poor Nutrition: Inadequate protein intake and malnutrition can hasten muscle loss.
4. Chronic Diseases: Conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), kidney disease, diabetes, cancer, and HIV can exacerbate sarcopenia.
5. Hormonal Changes: Reduction in hormone levels, particularly testosterone and insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1), plays a role in muscle fiber changes.
6. Insulin Resistance: Impaired ability to respond to insulin can contribute to muscle wasting.
7. Neuromuscular Changes: Decline in the number of nerve cells communicating with muscles affects movement.
To accurately diagnose sarcopenia, physiotherapists and osteopaths employ a comprehensive approach, integrating both clinical expertise and specialized assessments. The diagnostic process encompasses various elements:
By combining these diagnostic tools, physiotherapists and osteopaths gain a comprehensive understanding of the individual's musculoskeletal condition. This holistic approach informs tailored intervention strategies, emphasizing functional improvements and overall well-being.
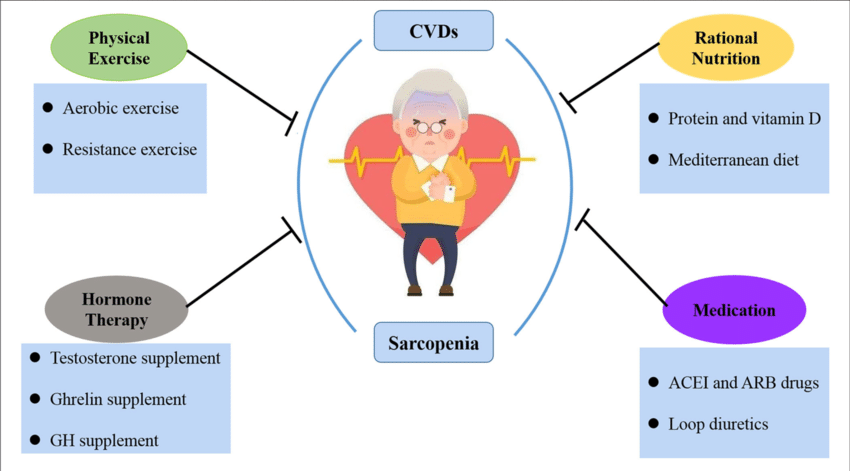
Addressing sarcopenia involves a multifaceted strategy tailored to each individual's unique needs. Physiotherapists and osteopaths collaborate to implement effective interventions that enhance muscle mass, strength, and overall functional capacity. The treatment plan encompasses several key components:
Sarcopenia management is a collaborative effort, with physiotherapists and osteopaths working in tandem to empower individuals with tailored strategies. By integrating lifestyle modifications, targeted exercises, and ongoing support, this comprehensive approach aims to optimize muscle health, enhance functional capacity, and improve overall quality of life.
In a pivotal move in 2016, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) officially recognized sarcopenia as a distinct disease. This recognition was solidified by the assignment of an International Classification of Disease (ICD-10) code, marking a significant milestone in healthcare. The designation facilitates accurate diagnosis and comprehensive reporting, enabling healthcare providers to effectively address and manage this condition.
Sarcopenia and muscle atrophy share commonalities but differ in crucial aspects. Sarcopenia, a subtype of muscle atrophy, is specifically associated with the aging process. It manifests as a dual challenge involving a reduction in both the size and number of muscle fibers. While muscle atrophy involves a decrease in fiber size, the number of fibers remains relatively constant. This distinction highlights the nuanced nature of muscle-related conditions and underscores the importance of precise diagnosis and targeted interventions.
As healthcare professionals continue to refine their understanding of sarcopenia, these clarifications aim to provide individuals with a clearer comprehension of the condition's distinct characteristics and its unique place within the spectrum of muscle-related health issues.
Sarcopenia poses a significant challenge, particularly in an aging population. Recognizing its symptoms, understanding preventive measures, and embracing a proactive approach to muscle health are crucial steps in mitigating its impact. Early diagnosis, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing research pave the way for improved management and treatment, offering a ray of hope for individuals navigating the complexities of sarcopenia.
Achilles tendinitis is a prevalent overuse injury that impacts the Achilles tendon—a critical band of tissue that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone.
Back pain is a prevalent and often debilitating condition that can affect individuals of all ages and walks of life.
Arthritis is a common and often painful condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It's not a single disease but rather a group of more than 100 different types of joint-related conditions.
Ankle injuries are prevalent in the world of sports and can be a significant setback for athletes.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), often referred to as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord.
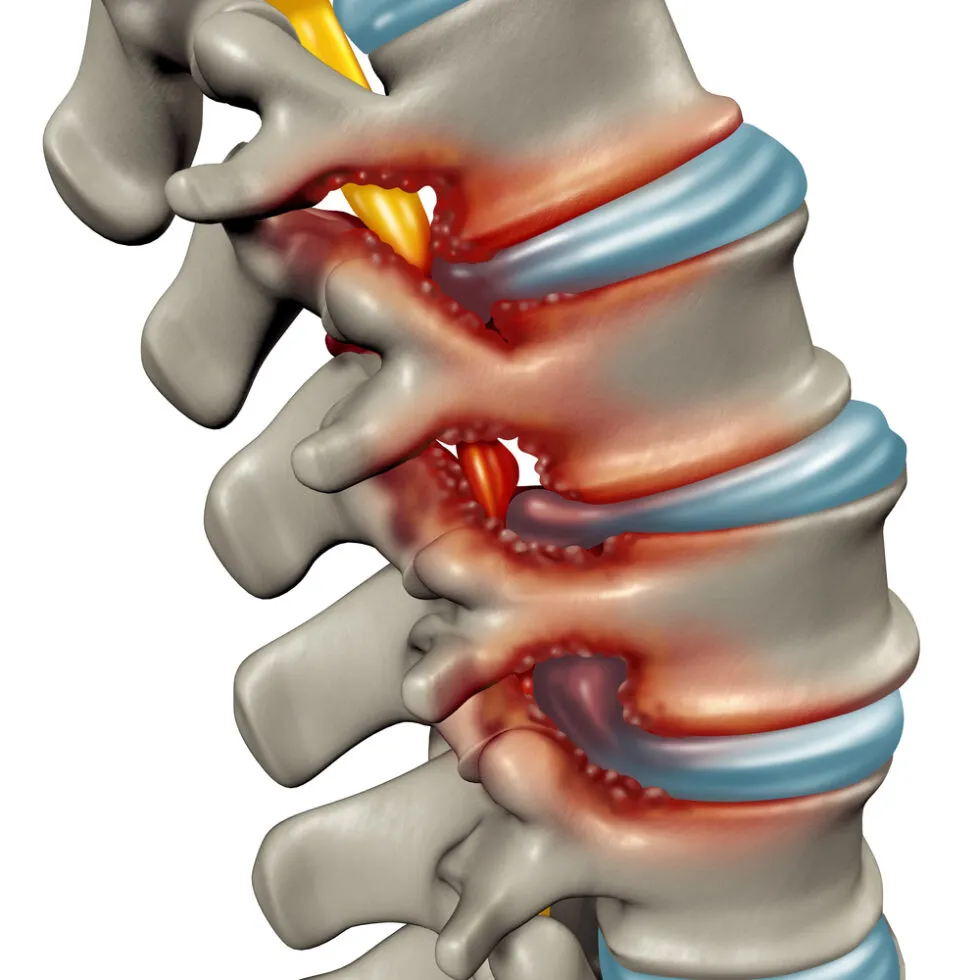
Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD) is a common condition that affects the intervertebral discs in the spine.
Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) is a perplexing and debilitating condition that impacts individuals, often altering their daily lives and challenging conventional understanding.
Muscular dystrophy encompasses a group of diseases leading to progressive muscle weakness and loss of muscle mass. The development of abnormal genes disrupts the production of necessary proteins crucial for healthy muscle function.
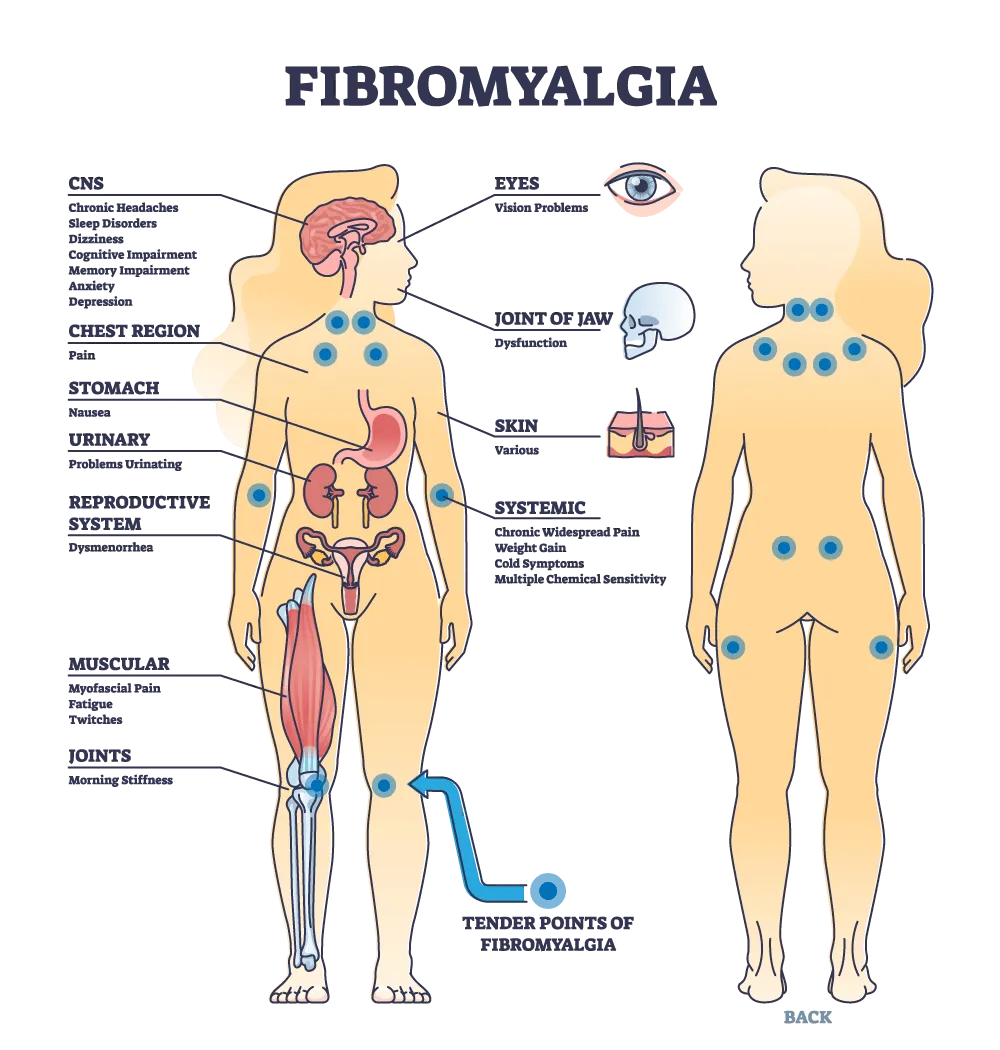
Fibromyalgia stands as a complex and often misunderstood condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbances
Bunions, medically referred to as "hallux valgus," are a common and often painful foot deformity that affects the joint at the base of the big toe.
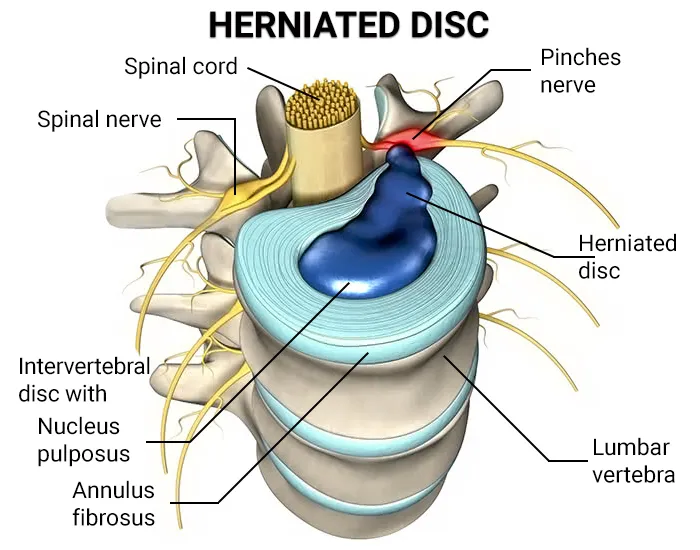
Herniated disc symptoms can be debilitating, causing pain, numbness, and mobility limitations.
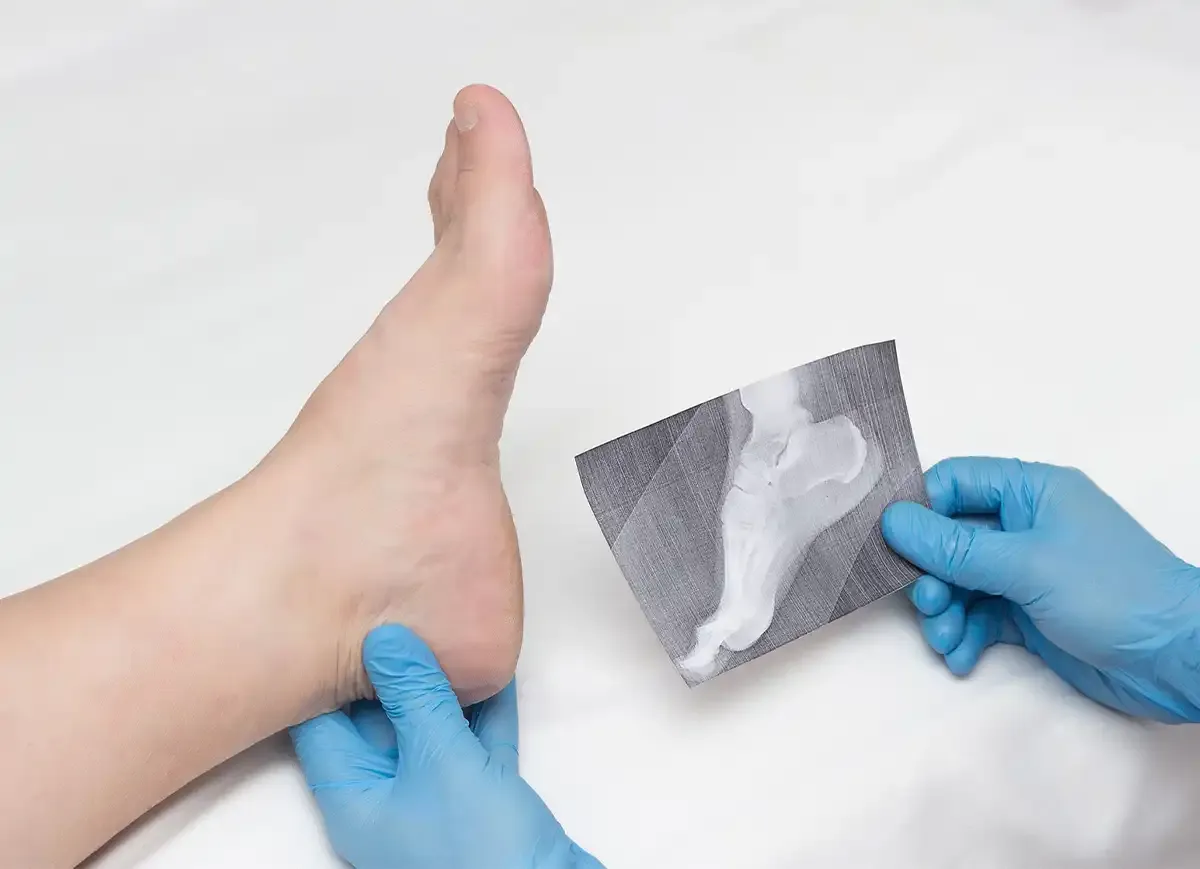
A heel spur is a bony growth that pokes out below your back heel bone inside of your foot. Heel spurs happen when stress and strain damages your foot ligaments.
Knee pain is a widespread issue that can significantly impact a person's mobility and quality of life.Knee pain is a widespread issue that can significantly impact a person's mobility and quality of life.
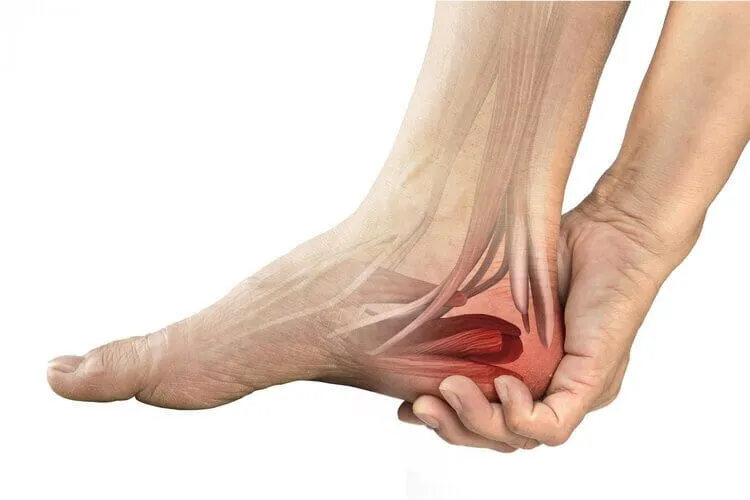
Heel pain can be a nagging and uncomfortable issue that affects many people. In this article, we will explore the various causes of heel pain, common symptoms associated with it, and the available treatments that can help you find relief and get back to your active lifestyle.
Military Neck, also referred to as Cervical Kyphosis, is a condition that affects the natural curvature of the cervical spine, resulting in the loss of its typical curve.
Migraines and headaches are prevalent neurological disorders that affect a significant portion of the population.

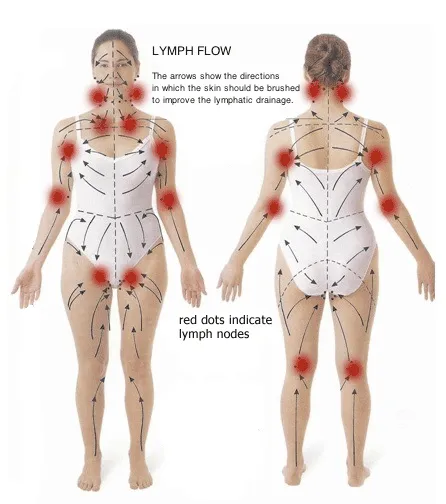
Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid, leading to persistent swelling, typically in the arms or legs.
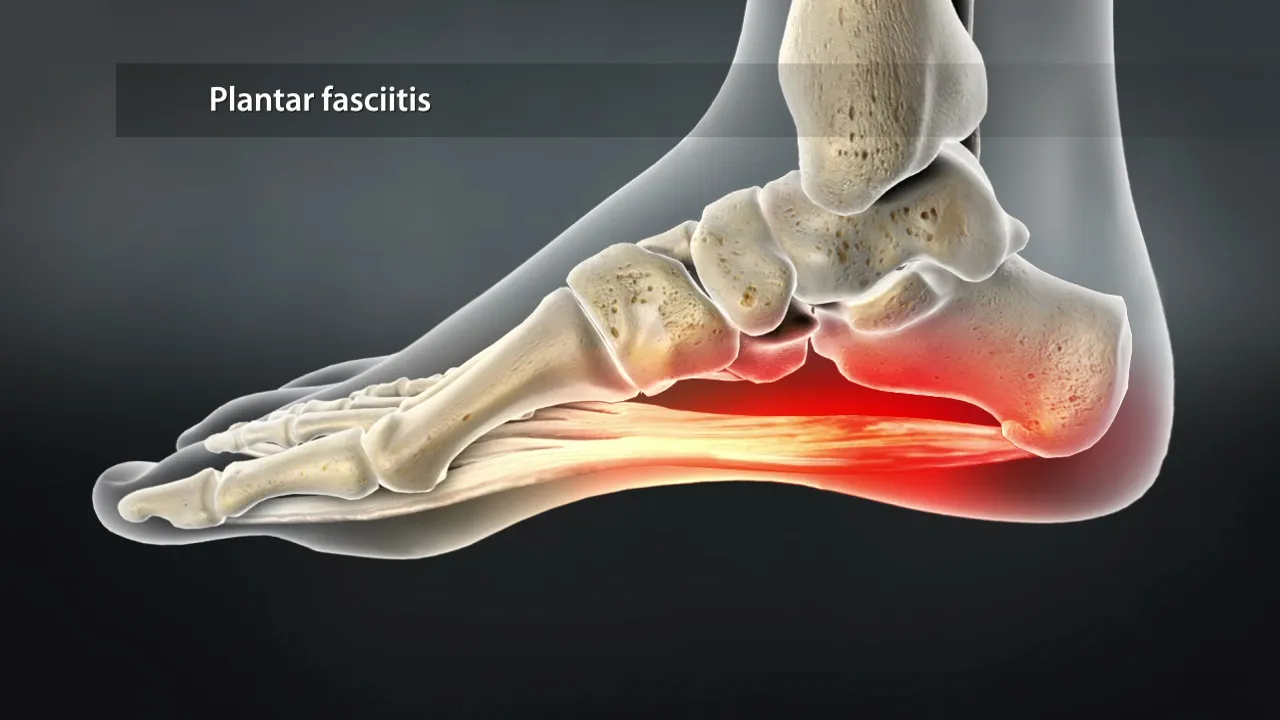
Plantar fasciitis is a common and often painful foot condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
Piriformis syndrome is a perplexing condition, often overshadowed by more common sources of hip and lower back pain.
motor vehicle accidents (MVA) can result in a wide range of injuries, from minor bruises to severe trauma. in the aftermath of such incidents, seeking prompt medical attention is crucial for assessing and addressing any injuries sustained.

Spinal stenosis, a prevalent spinal condition, is characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal, leading to discomfort and neurological symptoms.
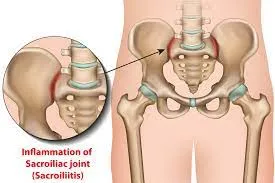
The sacroiliac joint, a crucial junction between the sacrum and the ilium bones in the pelvis, plays a pivotal role in supporting the weight of the upper body.
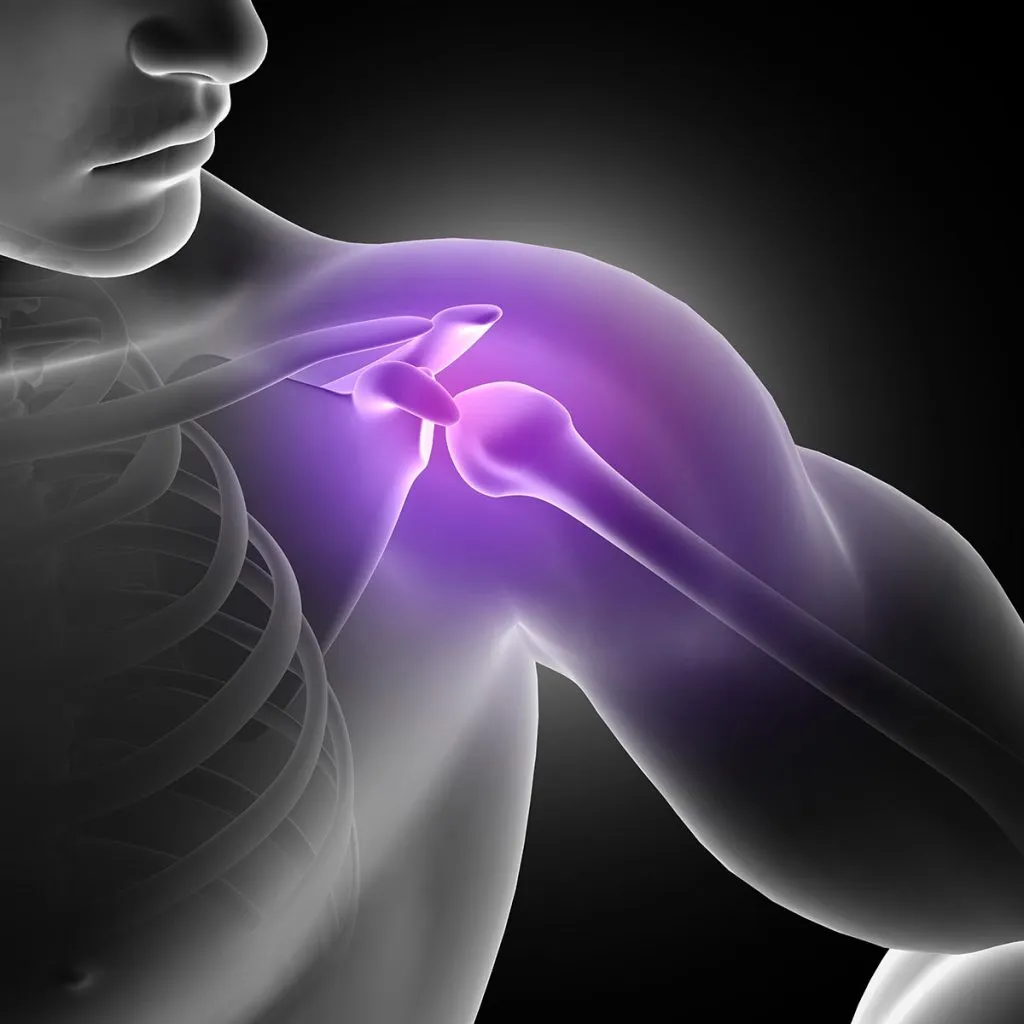
A rotator cuff injury can be a painful and limiting condition, impacting the functionality of the shoulder.
Suffering from lower back pain from sitting? It could be from poor ergonomics in your workplace. Learn more with these tips for how to alleviate pain from sitting.

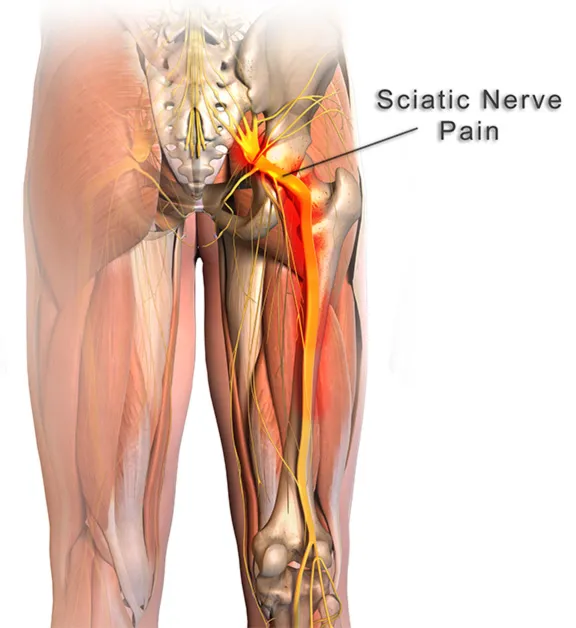
Sciatica is a painful and often debilitating condition that affects numerous individuals worldwide.
Gluteal tendinopathy is a condition that affects the tendons in the gluteal region, leading to pain and restricted mobility.
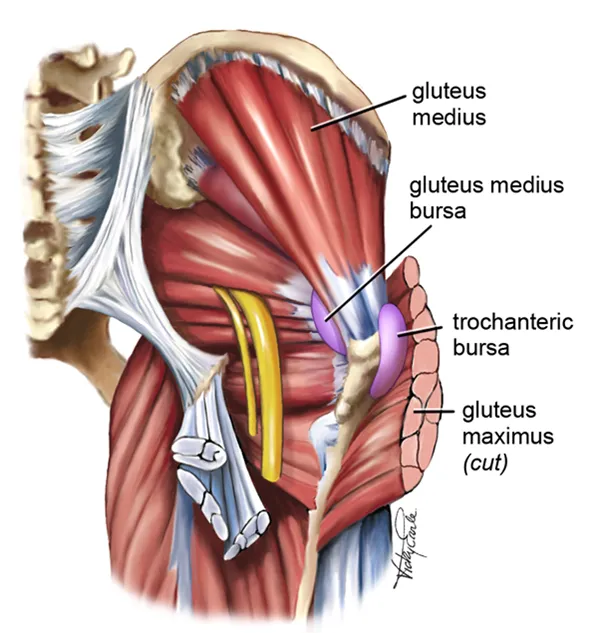
Tennis Elbow, also known as Lateral Epicondylitis, is a painful condition that affects the tendons in the forearm, causing discomfort and limited mobility in the elbow and wrist.

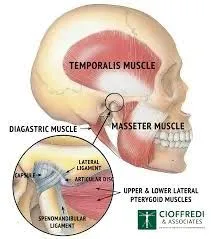
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) serves as a pivotal mechanism, allowing us to perform everyday activities such as speaking, chewing, and yawning with ease. However, when this complex joint encounters issues, it can lead to Temporomandibular Joint Syndrome (TMJ syndrome).
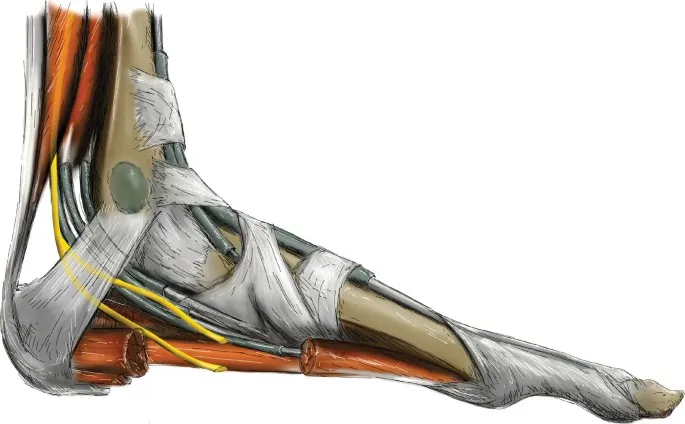
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome (TTS) is a common and often painful condition affecting the tarsal tunnel—a narrow passage in the ankle.
Explore the impact of time-restricted eating on heart health. Learn about the connection between diet and cardiovascular risk.
Most cases of foot or ankle pain are short term and are caused by soft tissue injuries, such as sprains or strains. You can usually ease the pain yourself But see York Rehab Clinic if the pain does not improve.
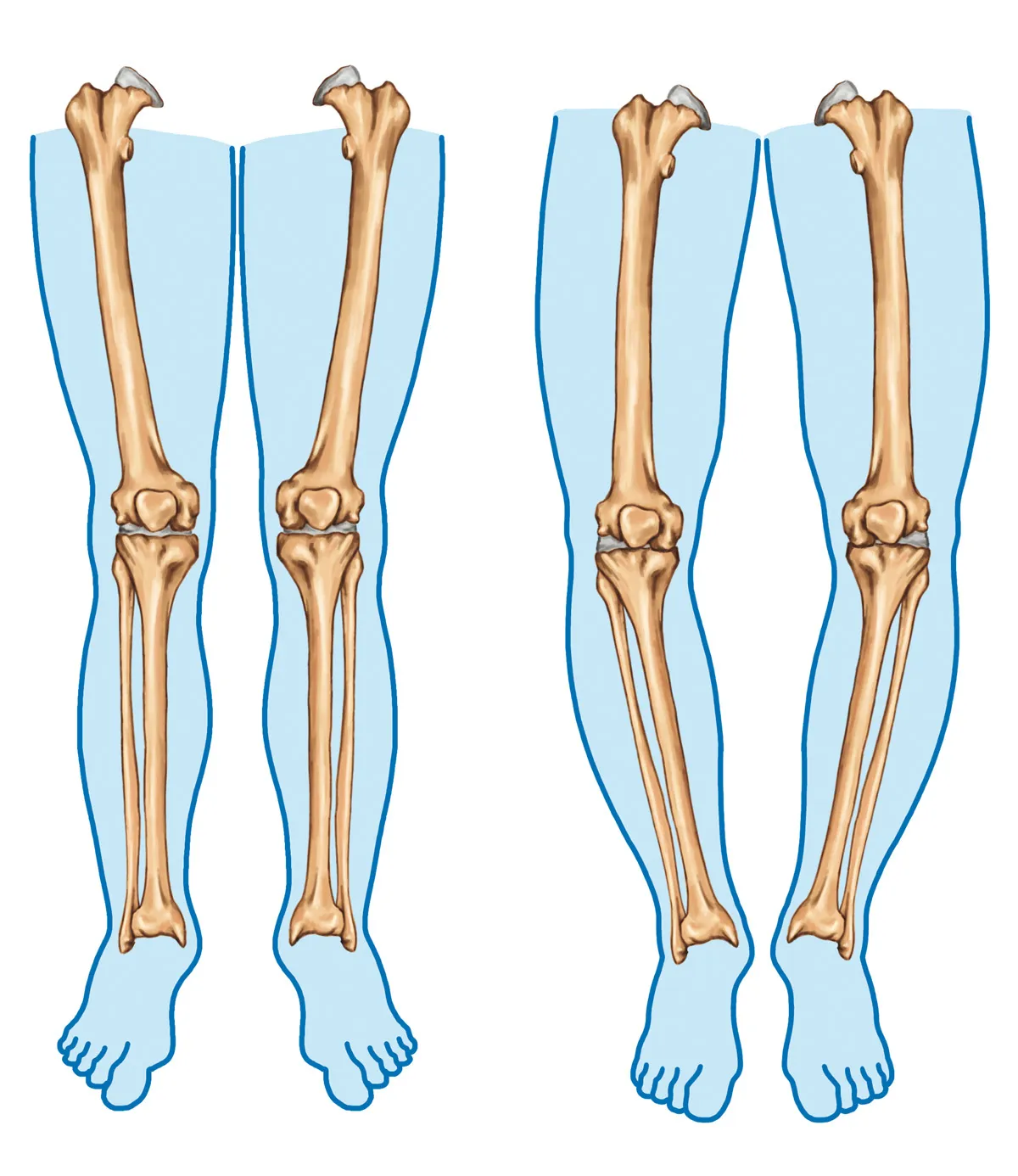
Bow legs is a genetic condition where the knees bow outward when standing. Learn its symptoms and causes at York Rehab Clinic.
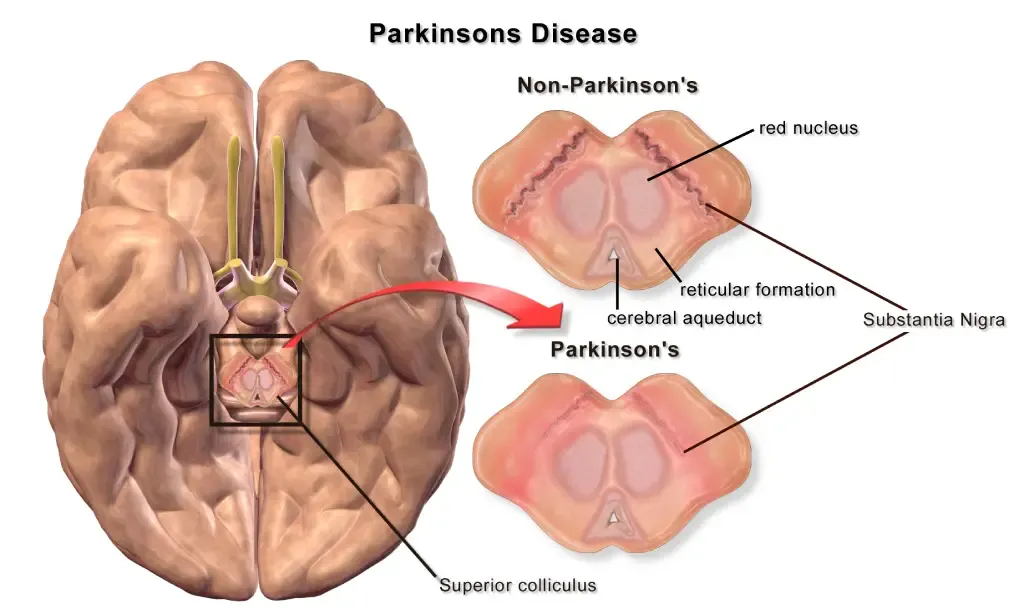
This article explores the complexities of Parkinson’s Disease and sheds light on the therapeutic benefits offered by osteopathy and physiotherapy.
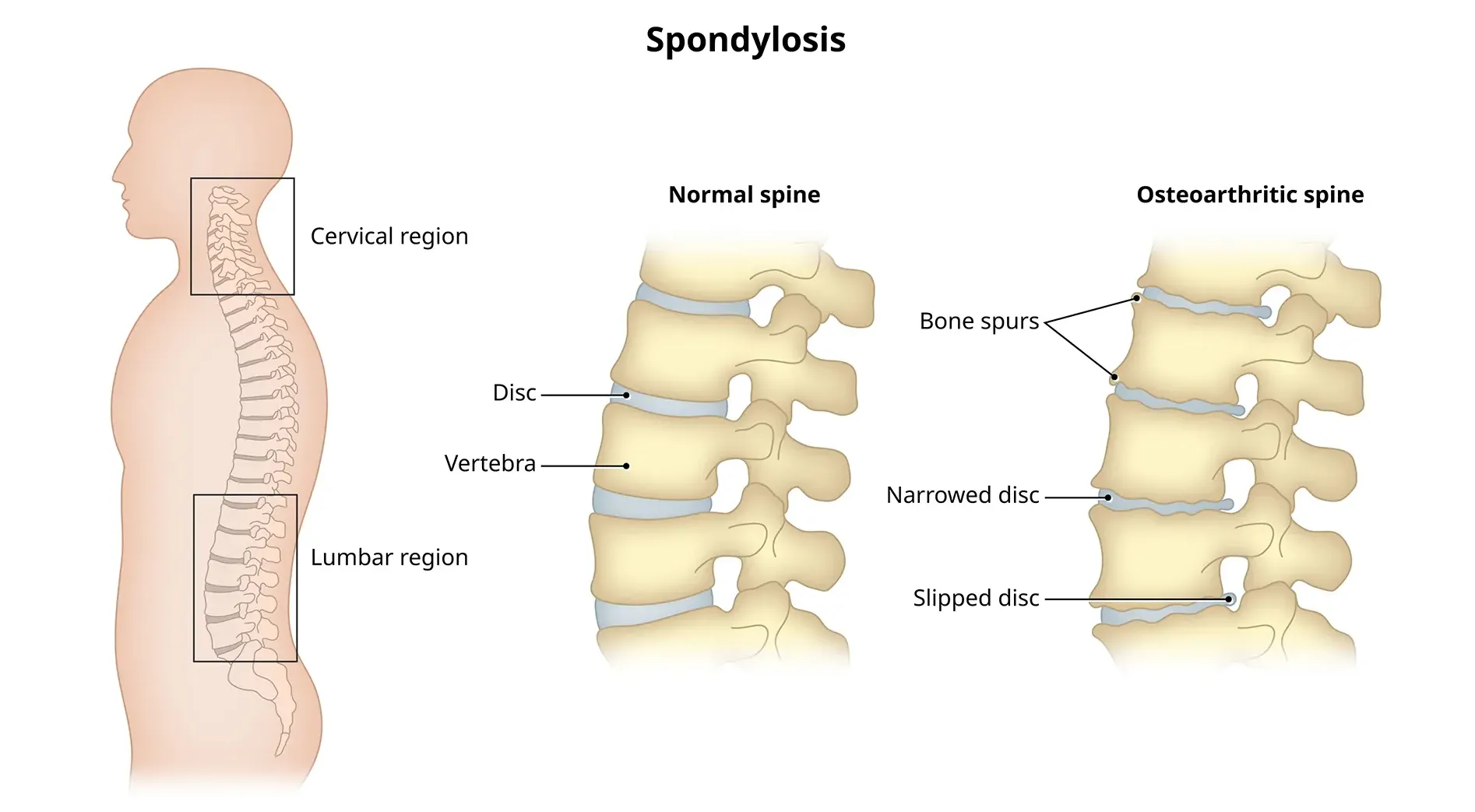
Cervical spondylosis, a prevalent condition, unfolds as a result of wear and tear on the spinal discs in the neck.
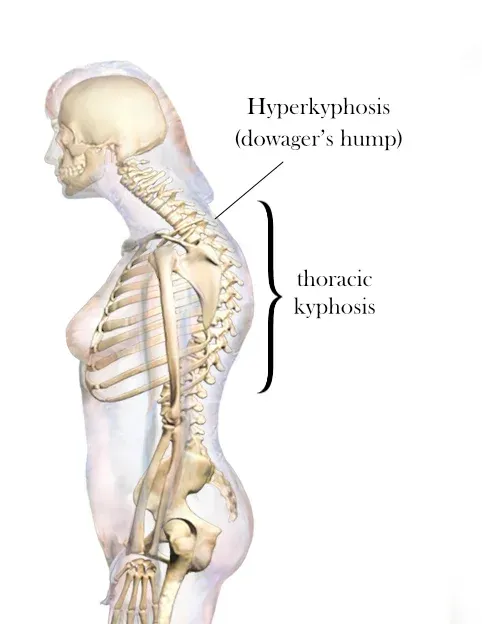
A dowager’s hump, a curve at the base of your neck, can cause extreme fatigue, back pain and headaches.
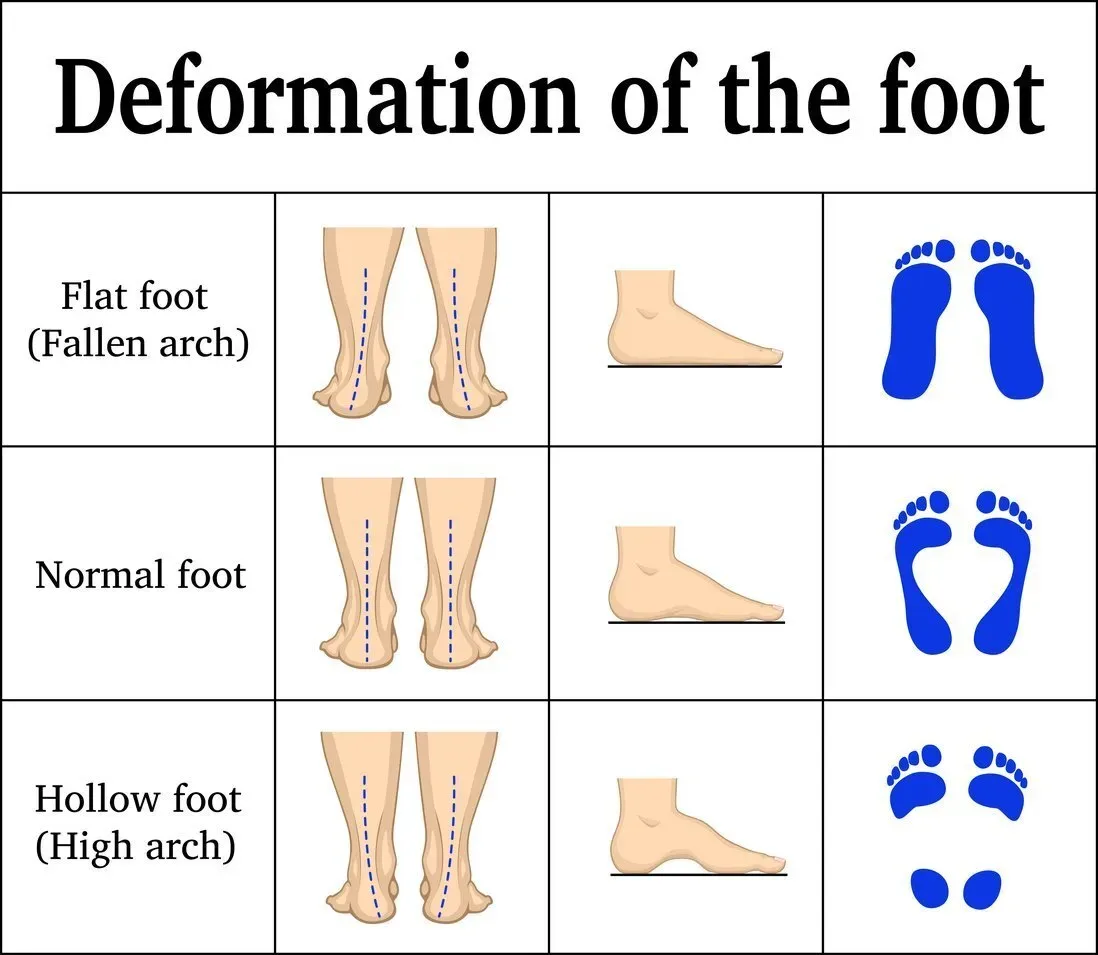
Flat feet cause pain, muscle strain, and fatigue. Treatments can ease discomfort. Symptoms include ankle pain, muscle fatigue and changes in walking.
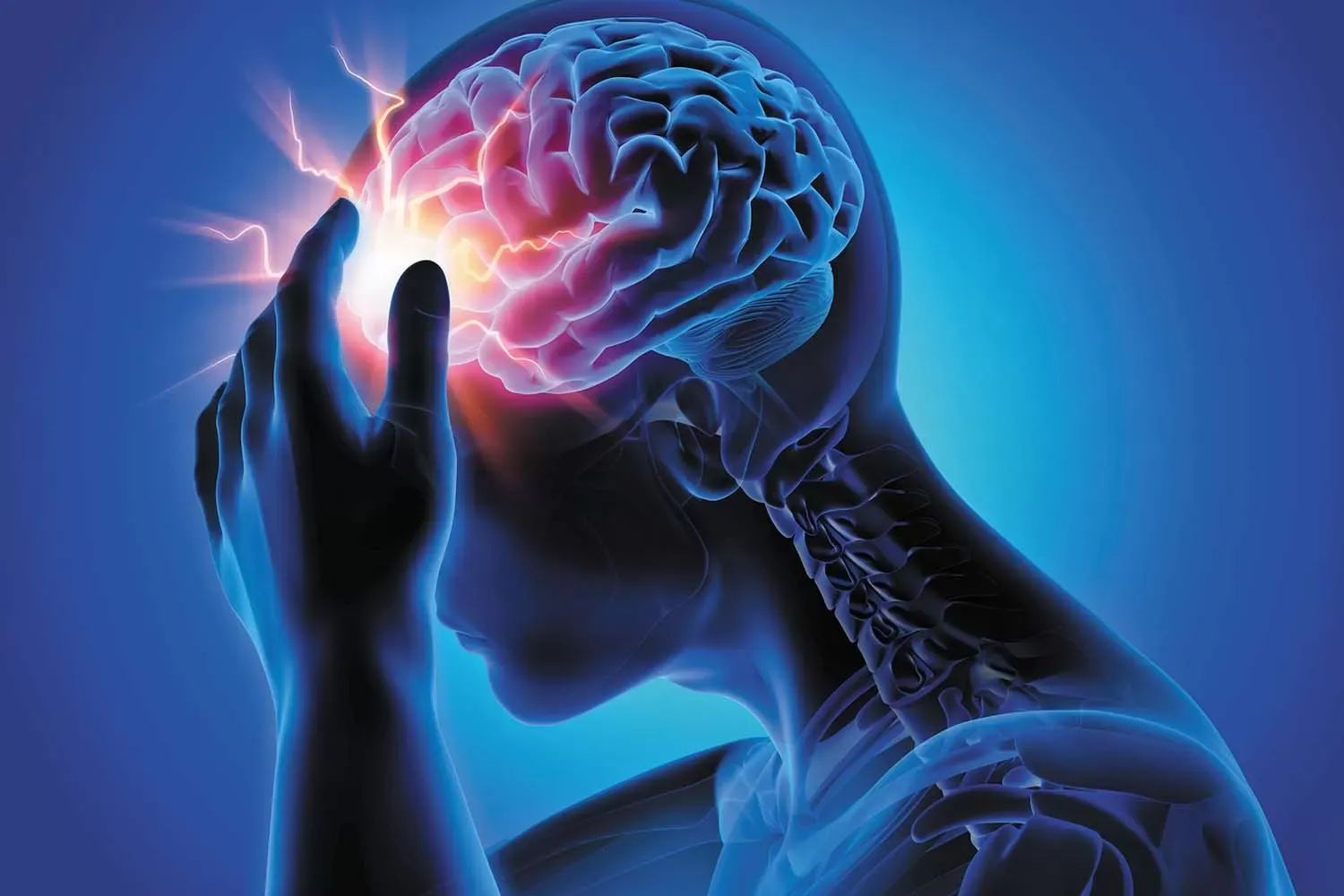
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) often results from a violent blow or jolt to the head or body, causing various physical and psychological effects.
Introduction: Neck stiffness can be a discomforting and limiting condition that affects people of all ages.